Ocean and Coastal Fishing Industry Dominated the Fishing Sector
There were an estimated total number of 1,129 fishing establishments in the entire country, according to the results of the 2002 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry. Majority (82.2 percent or 928 establishments) were accounted by fishing establishments with average total employment (ATE) of less than 20 workers. The remaining 17.8 percent comprised of 201 fishing establishments with ATE of 20 and more workers.
Ocean and coastal fishing industry ranked highest in terms of the number of establishments with 640 or 56.7 percent of the total count. Inland fishing industry, including the operation of fish farms and nurseries, and establishments engaged in pearl culture and shell gathering, seaweed farming and service activities incidental to fishing came second and third with respective shares of 295 establishments or 26.1 percent and 117 establishments or 10.4 percent of the total. The least number of establishments with 77 or 6.8 percent establishments were engaged in prawn culture. Figure 1 shows the distribution of fishing establishments by industry.
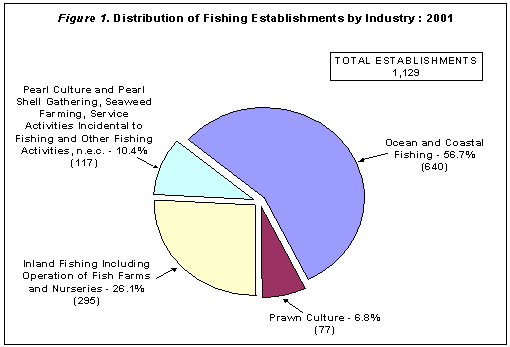
... Likewise Absorbed the Bulk of Fishery Workers
Total employment generated during the year 2001 was placed at 27,035. Fishing establishments with ATE of 20 or more workers employed the biggest number of workers at 17,930 representing 66.3 percent of total employment.
The ocean and coastal fishing industry, having the highest number of establishments, absorbed the bulk of workers numbering to 19,991 or equivalent to 73.9 percent of the total. This was followed by establishments engaged in inland fishing, including the operation of fish farm and nurseries with 3,825 workers representing share of 14.1 percent to total employment. Figure 2 displays the distribution of employment by industry.
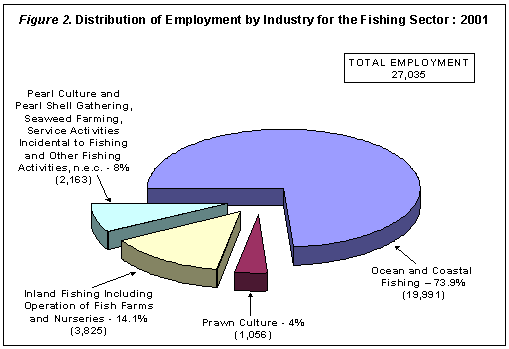
Average Monthly Compensation of Fishery Worker was P4,937
Total compensation paid during the year 2001 amounted to P1.5 billion or translated to an average monthly compensation of P4,937 per fishery worker.
Ocean and coastal fishing industry paid the highest average monthly compensation to each worker amounting to P5,253 while inland fishing industry paid the lowest at P3,598. Figure 3 shows average monthly compensation by industry.
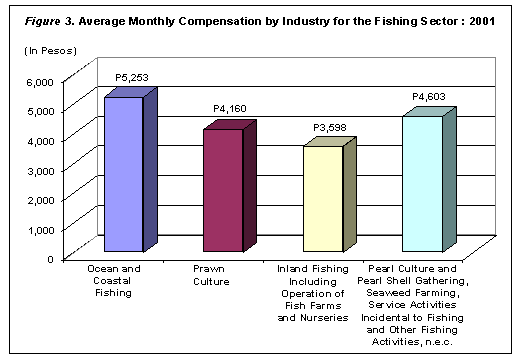
Total Revenue Amounted to P7.4 Billion
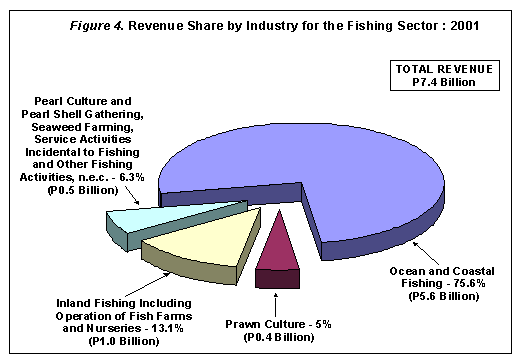
Total revenue earned by the fishing sector during the year 2001 was estimated at P7.4 billion with ocean and coastal fishing industry capturing more than three-fourths (75.6 percent) of revenue share amounting to P5.6 billion. Figure 4 shows the revenue share by industry for the fishing sector.
On the other hand, total operating cost, which is the sum total of compensation (P1.5 billion) and cost (P5.5 billion), amounted to P7.0 billion
The revenue to operating cost for all fishing establishments stood at 1.06. The prawn culture industry showed the best business performance among industries during the year 2001 as they earned the highest at the average of P1.21 for every peso spent.
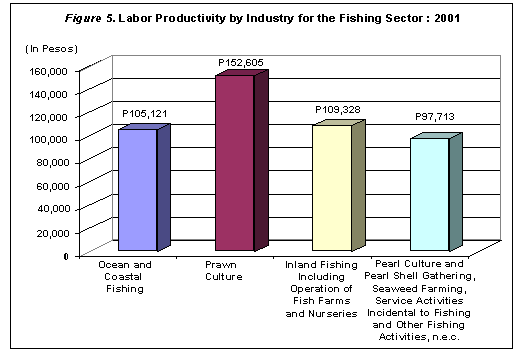
Labor Productivity was Highest for the Prawn Culture Industry
Labor productivity for the sector, measured as the ratio of value added per paid employee, was estimated at P106,984.
Workers in the prawn culture industry produced the highest labor productivity for the sector valued at P152,605. Figure 5 shows the labor productivity by industry.
___________________________________________________________________________________
TECHNICAL NOTES
Scope and Coverage
The 2002 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) aimed to collect and generate information on the levels, structure and trends of industries and businesses in the entire country. It has the calendar year, 2001, for its reference period. One of the 14 sectors covered in the survey is the fishing sector.
All fishing establishments with average total employment (ATE) of 20 and more workers were covered on a 100 percent basis and those with ATE of less than 20 workers were selected using stratified systematic random sampling.
Response Rate
The response rate is 88.4 percent of the 215 sample establishments for the fishing sector. Adjustments for non-response were made through imputations.
Concepts and Definition of terms
Establishments - An economic unit under single ownership or control, i.e., under a single legal entity, engaged in one or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location, and having permanency of assets in its premises during the operation. It is also defined as the unit that is engaged in the production of the most homogenous group of goods and services, usually at one location, but sometimes over a wider area, for which separate records are available that can provide data concerning the production of these goods and services and the materials, labor and physical resources used in this production.
Fishing Establishments - A farm or company engaged in ocean, coastal and inland fishing; fish farms, fishpond, fishpen; pearl farms and other fishery activities.
Economic activity or business - is the activity of the establishment as classified under the 1994 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). Generally, the main activity of the establishment is the establishmens' principal source of income. If the establishment is engaged in several activities, its main activity is that which earns the biggest income or revenue.
Average total employment (ATE) - is the sum of the number of persons who worked in or for this establishment for all months of the year divided by 12, regardless of the number of months the establishment is in operation.
Total Employment - includes all persons who worked in or for the establishment as of November 15, 2001.
Paid employees - are all persons working in the establishment and receiving pay, as well as those working away from the establishment paid by and under the control of the establishment. Included are all employees on sick leave, paid vacation or holiday. Excluded are consultants, home workers, workers receiving pure commissions only and workers on indefinite leave.
Working owners - owners who are actively engaged in the management but do not receive regular pay, i.e., not included in the payrolls. Managers and directors of corporations working for pay are reported as managers.
Unpaid workers - are persons working for at least one-third of the working time normal to the establishment and do not receive regular pay.
Salaries and wages - payments in cash or in kind to all employees, prior to deductions for employee's contributions to SSS/GSIS, withholding tax, etc. Included are total basic pay, overtime pay and other benefits.
Overtime Pay - are payments given for extra hours worked.
Other benefits - include bonuses, cost of living allowances, commutable transportation and representation allowances, food, housing, commissions paid to salaried employees, separation, retirement, terminal pay, gratuities, etc. Excluded are cost of uniform/working clothes and reimbursable transportation and representation allowances.
Employer's Contribution to SSS/GSIS and the like - to payments made by the establishment on behalf of the employees. Examples are SSS, GSIS, Employees Compensation Commission (ECC), Philhealth and PAGIBIG.
Revenue - includes cash received and receivables for goods sold and services rendered. Valuation is at producer's prices (ex-establishment), net of discounts and allowances, including duties and taxes but excluding subsidies.
Cost - refers to all expenses incurred during the year whether paid or payable. Valuation is at market prices including taxes and other charges, net of rebates, returns and allowances. Goods and services received by the establishment from other establishments of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Indirect taxes - refer to all taxes, other than income tax, incidental to the production or sale of goods and services, which are chargeable as expenses including business license, BIR stamps, real estate tax and other local taxes.
Subsidies - are all special grants in the form of financial assistance or tax exemption or tax privilege given by the government to aid and develop an industry or production and to protect it against competition.
Fixed assets - are physical assets expected to have productive lives of more than one year and intended for use and/or being used by the establishment. Included are land, buildings, other structures and land improvements, transport equipment, computers and peripherals, telecommunications equipment and apparatus, other machinery and equipment including furniture and fixtures, and cultivated assets.
Cultivated assets - include livestock for breeding, layers, dairy and working animals, orchards and other plantation of trees, standing timber and permanent crops.
Book value of fixed assets - is the initial value or acquisition cost of fixed assets less the accumulated depreciation.
Depreciation - is the total amount set aside for the year to cover the decrease in value of fixed assets owned by the establishment because of foreseen obsolescence, wear and tear as a result of operation and normal amount of accidental damage.
Capital expenditures - for fixed assets include cost of acquisition of new and used fixed assets; fixed assets produced by the establishment for its own use; major alterations, additions and improvements to fixed assets, whether done by others or on own account. Fixed assets received from other establishments belonging to the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Gross additions to fixed assets - is equal to capital expenditures less sale of fixed assets, including land.
Inventories - refer to the stock of goods owned by and under the control of the establishment as of a fixed date, regardless of where the stocks are located. Valuation should be at current replacement cost in purchaser's (market) prices. Replacement cost is the cost of an item in terms of its present price rather than its original cost.
Finished products inventory - refer to the goods made by the establishment which are ready for sale/shipment as of a reference date. Valuation is at producer's price.
Work-in-process inventory - refers to the value of all materials which have been partially processed by the establishment but which are not usually sold or turned over to other establishment without further processing. Valuation is at producer's price.
Change in inventories - is computed as the total value of ending inventory less the total beginning inventory.
Census value added - represents the difference between the value of output and total costs of materials and supplies consumed, fuels purchased, electricity purchased, industrial services done by others and goods purchased for resale.
Value added - represents the sum of census value added and value of non-industrial services done for others less the cost of non-industrial services done by others and other costs.
Detailed Statistical Tables
The detailed tables at the national and regional levels are available upon request from the Industry Statistics Division, National Statistics Office, 4th Floor Solicarel Bldg II, Ramon Magsaysay Blvd., Sta. Mesa, Manila Tel. No. (062) 716-39-32.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
