Miscellaneous business activities leads the sector
- The 2005 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry covered a total of 42,681 establishments engaged in real estate, renting and business activities. About 40,593 or 95.1 percent of the total figure were establishments with average total employment (ATE) of less than 20 while 2,088 or 4.9 percent were establishments with ATE of 20 or more.
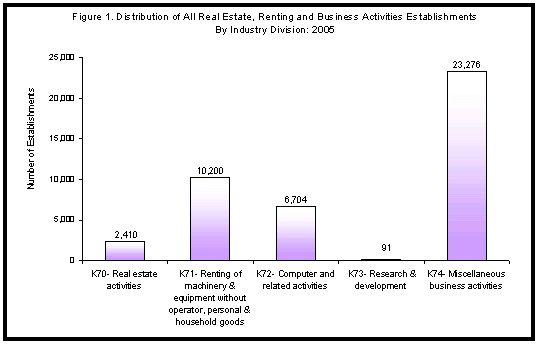
- Among the industry divisions, miscellaneous business activities (K74) like legal, accounting, bookkeeping activities; advertising; investigation and security activities; and related technical consultancy comprised the largest number of establishments accounting for more than half (23,276 or 54.5%) of the sector’s total. Renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71) took the second place with 10,200 or 23.9 percent and computer and related activities (K72) was third, with 6,704 or 15.7%. On the other hand, research and development (K73) had the least number with only 91 establishments (0.2%). Figure 1 shows the sector’s distribution of establishments by industry division.
Miscellaneous business activities employ the biggest number of workers
- The sector employed a total workforce of 475,650 workers in 2005. Of the total, 434,760 (91.4%) were paid employees and 40,890 (8.6%) were working owners or unpaid workers.
- Being the largest in number of establishments, miscellaneous business activities (K74) employed almost four-fifths (373,895 or 78.6%) of the total workforce.
- Computer and related activities (K72) and renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71) followed next with 40,110 or 8.4 percent and 34,257 or 7.2 percent, respectively. Meanwhile, research and development (K73) registered the least with 2,390 workers or 0.5 percent.
Employees of computer and related activities receive the highest monthly pay
- In 2005, the sector paid a total compensation of Php60.9 billion, equivalent to an average monthly pay of Php11, 669 per paid employee.
- Industry wise, miscellaneous business activities (K74) paid the highest compensation of about Php46.6 billion accounting for more than three-fourths (76.5%) of the sector’s total. Computer and related activities (K72) placed second with Php8.4 billion (13.8%). Real estate activities (K70) ranked third with Php4.3 billion (7.1%). In contrast, research and development (K73) reported the lowest amount of Php306.9 million (0.5%).
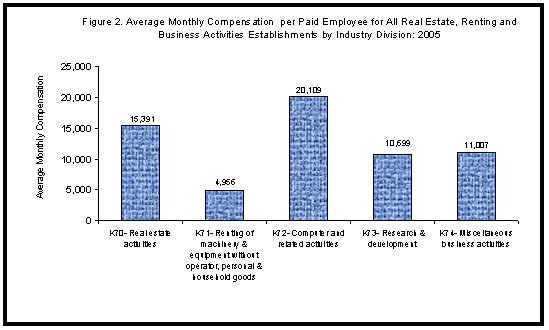
- Employees of computer and related activities (K72) received the highest monthly compensation of Php20,109; followed by those involved in real estate activities (K70), Php15,391 and miscellaneous business activities (K74), Php11,007. However, workers in renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71) received the lowest monthly pay of Php4,956. Figure 2 displays the average monthly compensation per paid employee by industry division.
Miscellaneous business activities contribute the biggest share in revenue and costs
- Gross revenue realized by the sector reached Php221.5 billion in 2005.
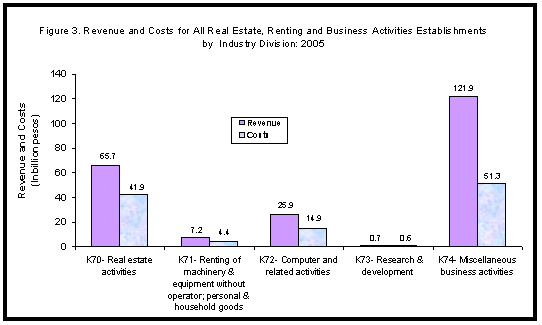
- Bulk of the revenue was generated by establishments engaged in miscellaneous business activities (K74) with Php121.9 billion (55.1%). Real estate activities (K70)) came next with Php65.7 billion (29.7%). On the other hand, research and development (K73) had the least share with Php737.9 million (0.3%).
- Total operating costs and expenses (excluding compensation paid to employees) incurred by the sector amounted to Php113.1 billion in 2005.
- Having the biggest share in revenue, miscellaneous business activities (K74) and real estate activities (K70) also had the largest proportion in costs with Php51.3 billion (45.4%) and Php41.9 billion (37.1%), respectively. On the contrary, research and development (K73) incurred the least cost of Php598 million (0.5%). Figure 3 shows the sector’s distribution of revenue and costs by industry division.
Revenue per peso cost is valued at Php1.96
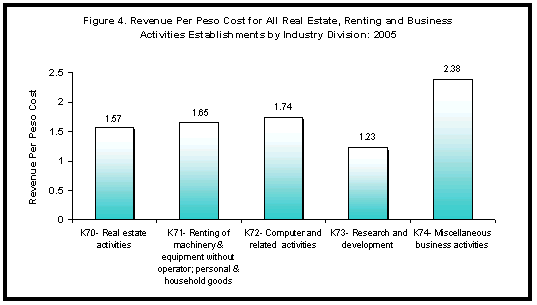
- For every peso spent, Php1.96 was earned by the real estate, renting and business activities sector.
- The highest revenue per peso cost was registered in miscellaneous business activities (K74) at Php2.38; while the lowest, in research and development (K73), at Php1.23. Figure 4 shows the revenue per peso cost by industry division.
Value added totals to Php133.5 billion
- Total value added derived by real estate, renting and business activities sector totaled to Php133.5 billion in 2005.
- Among the industry divisions, miscellaneous business activities (K74) reported the highest value added comprising more than three-fifths (Php81.8 billion or 61.2%) of the total. Real estate activities (K70) ranked second with Php34.6 billion (25.9%) and computer and related activities (K72) ranked third with Php13.2 billion (9.9%). On the other hand, research and development (K73) derived the least value added with Php223.6 million (0.2%).
Gross additions to fixed assets reach Php13 billion
- Gross additions to fixed assets (capital expenditures less sale of fixed assets) acquired by the sector reached Php13 billion in 2005.
- Miscellaneous business activities (K74) registered the highest gross additions to its fixed assets with Php7.8 billion (60.1%). Real estate activities (K70) followed with Php3.7 billion (28.7%). On the other hand, research and development (K73) recorded the least with only Php24.7 million (0.2%).
Change in inventories amounts to Php3.9 billion
- Total change in inventories (ending less beginning inventory) amounted to Php3.9 billion in 2005.
- All industries, except renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71), recorded a positive change in inventories. Real estate activities (K70) comprised 93.9% (Php3.7 billion) of the total change in inventories.
Subsidies granted by government amount to Php394.9 million
- Total subsidies granted by government to support real estate, renting and business activities sector amounted to Php394.9 million in 2005.
- Miscellaneous business activities (K74) received the largest amount of subsidies with Php184.4 million, equivalent to more than two fifths (46.7%) of the total figure. Research and development (K73) closely followed with Php121.2 million (30.7%). However, no subsidy was granted to establishments involved in renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71).
TECHNICAL NOTES
Scope and Coverage
The 2005 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) formerly known as Annual Survey of Establishments (ASE) was conducted to collect information on the structure and trends of economic activities in the entire country for the year 2005. Covered were establishments engaged in economic activities as defined under the 1994 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC).
These establishments were classified into 14 sectors one of which is on Real Estate, renting and business activities (Sector K), which covered all establishments, except those engaged in letting and operating real estate such as residential and non-residential buildings and land rentals. The sector is composed of establishments engaged in five industry divisions, namely, real estate activities (K70); renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods (K71); computer and related activities (K72); research and development (K73) and miscellaneous business activities (K74).
All real estate, renting and business activities establishments nationwide with average total employment (ATE) of 100 and over were covered on a 100 percent basis and those with ATE less than 100 were selected using simple random sampling; except business process outsourcing (BPO) establishments, all of which were taken as samples regardless of size (ATE).
Response Rate
A total of 2,417 or 97.2 percent responded out of the 2,487 samples drawn for the sector but effective response rate is 55.4% percent. Adjustments for non-responses were made through imputations.
Concepts and Definition of terms
Establishment - an economic unit, which engages under a single ownership or control, i.e. under a single legal entity, in one, or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location. It is also defined as the unit that is engaged in the production of the most homogenous group of goods and services, usually at one location, sometimes over a wider area for which separate records are available that can provide data concerning the production of these goods and services and the materials, labor and physical resources used in the production.
Economic activity or business - is the activity of the establishment as classified under the1994 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). The main activity refers to the activity that contributes the biggest or major portion of the gross income or revenue of the establishment.
Effective response rate - is computed by dividing the total number of samples with good report, partial report, and report obtained from secondary sources, such as QSPBI, MISSI and financial statements from SEC and those extracted from consolidated report of related establishment; by the total number of samples for the sector.
Real estate establishment - Realtor, developer, agency, broker, lesser or companies engaged in the operating, developing, subdividing, buying and selling of real estate.
Renting of machinery and equipment without operator; personal and household goods establishment - Office or firm engaged in renting and leasing of transport equipment; agricultural, construction, engineering and office machinery and equipment; computers and computer peripherals equipment; wearing apparel; furniture; electrical appliances; audio-video machines, tapes and records; sports and recreational equipment; books, journals and magazines; ornamental plants and other personal and household goods.
Computer and related activities establishment - Office or firm engaged in hardware consultancy, software publishing, software development, data processing, database activities and on-line distribution of electronic content, maintenance and repair of office, accounting and computing machinery and others.
Research and development establishment - Office or firm engaged in research and development in natural sciences, engineering and technology, agricultural sciences, health sciences, social sciences, humanities and others.
Miscellaneous business activities establishment - Office or firm engaged in legal, accounting, bookkeeping and auditing; tax consultancy; market research and public opinion polling; business and management consultancy; architectural and engineering activities; land surveying services; technical and testing analysis; advertising; labor recruitment and provision of personnel; investigation and security services; cleaning of buildings of all types; pest control services; industrial cleaning activities; photographic activities; packaging activities; management and administrative services; bill collecting and credit rating services; business brokerage; stenographic, duplicating and mailing activities; fashion design; interior decoration services; call center activities; medical transcription and others.
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is the leveraging of technology or specialist process vendors to provide and manage an organization’s critical and/or non-critical enterprise processes and applications. The most common examples of BPO are call centres, human resources, accounting and payroll outsourcing. Business process outsourcing may involve the use of off-shore resources.
Outsourcing (or contracting out) is the delegation of non-core operations or jobs from internal production within a business to an external entity (such as a subcontractor) that specializes in that operation. Outsourcing is done to save money, improve quality, or free company resources for other activities. Outsourcing was first done in the data-processing industry and has spread to areas, including telemessaging and call centers. Outsourcing is the wave of the future.
Offshore outsourcing is the practice of hiring an external organization to perform some or all business functions in a country other than the one where the product or service will be sold or consumed.
Total Employment - is the number of persons who worked in or for the establishment as of November 15, 2005.
Paid employees - are persons working in the establishment receiving regular pay as well as those working away from the establishment when paid by and under the control of the establishment. Included are persons working as full-time or part-time and those employees on sick leave, paid vacation or holiday. Excluded are consultants, home workers and workers receiving commission only.
Unpaid workers - include working owners who do not receive regular pay, apprentices and learners without regular pay, and persons working without regular pay for at least one third of the working time normal to the establishment.
Salaries and wages - are payments in cash or in kind, prior to deduction for employee’s contribution to SSS/GSIS, withholding tax, etc. Included are total basic pay, vacation, sick, maternity leave pay, overtime pay, and other benefits.
Revenue - refers to cash received and receivables for goods sold and services rendered.
Cost - refers to all expenses excluding compensation incurred during the year whether paid or payable. Valuation should be at market price including taxes and other charges, net of discounts, rebates, returns and allowances. Goods received from and services rendered by other establishment of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Gross additions to fixed assets - refer to the cost of acquisition of fixed assets acquired in 2005 less the value of sales of fixed assets during the year.
Fixed assets - are physical assets expected to have productive life of more than one year and intended for use and/or being used by the establishment. Included are land, buildings, fixtures, machinery, tool, furniture, office equipment, vehicles, and the like.
Capital expenditures - refer to the cost of acquisition of fixed assets acquired in 2005 whether or not full payments have been made.
Subsidies - are special grants in the form of financial assistance or tax exemption or tax privilege given by the government to develop an industry or production and to protect it against competition.
Inventories - refer to stocks of goods owned by or under the control of the establishment as of a fixed date, regardless of where the stocks are located. Valuation should be at current replacement cost in purchaser’s price at the indicated dates. Replacement cost is the cost of an item in terms of its present price rather than its original price.
Change in Inventories - is a derived indicator, computed as the value of ending inventory less the value of beginning inventory.
Value Added - is equal to the sum of total revenue, cost of fixed assets produced on own account, change in inventory of real estate for sale and change in inventory of materials, supplies and fuels less the following items: cost of materials and supplies purchased; cost of real estate purchased for sale; cost of fuels purchased to run motor vehicles, machinery and other equipment; cost of electricity purchased; cost of industrial services done by others; cost of non-industrial services done by others; cost of computer software expenses; cost of research and experimental development; and other costs (for real estate activities).
Value Added is also equal to the sum of total revenue, cost of fixed assets produced on own account and change in inventory of materials, supplies and fuels, less the following items: cost of materials and supplies purchased; cost of fuels purchased to run motor vehicles, machinery and other equipment; cost of electricity purchased; cost of industrial services done by others; cost of non-industrial services done by others; cost of computer software expenses; cost of research and experimental development; and other costs (for industries other than real estate activities).
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
