Majority of establishments have an average total employment of less than 20
-
The number of establishments in private education service activities reached 8,900 in 2003. Establishments with an average total employment (ATE) of less than 20 dominated the sector with 6,813 or 76.6 percent of the total. The remaining 2,087 establishments or 23.4 percent had an average total employment of 20 and over. (See table 1 to table 3.)
-
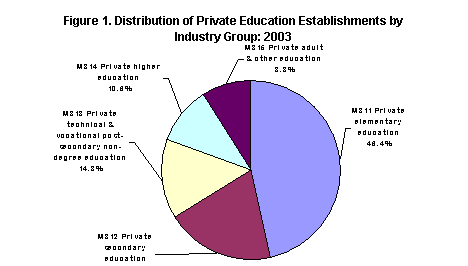
Establishments involved in private elementary schools (PSIC M811) recorded the biggest number of establishments accounting for 4,129 or 46.4 percent of the total. Private secondary schools ranked second, with 1,719 establishments (19.3%) while private technical and vocational post-secondary non-degree education (PSIC M813) followed with 1,321 establishments (14.8%). Figure 1 shows the distribution of private education establishments by industry group.
Establishments providing private higher education employ the most number of workers
-
In 2003, total employment of establishments engaged in private education activities registered a total of 249,680. Of this, 244,540 or 97.9 percent were paid employees while 5,176 or 2.1 percent were working owners and unpaid workers. Distribution of employment by industry group is shown in Figure 2.
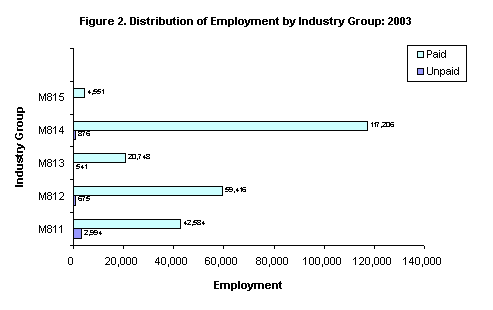
-
Private higher education establishments absorbed the most number of workers with 118,082 or 47.3 percent of the total. Private secondary education establishments ranked second employing 60,091 workers (24.1%), followed by private elementary education establishments with 45,578 employees (18.3%)
Private higher education employees receive the highest average monthly compensation
-
Total compensation paid by private education service establishments amounted to Php33.3 billion which was equivalent to an average monthly compensation of Php11, 352 per paid employee.
-
Private higher education employees were the highest earners with an average monthly pay of Php14,141. Employees in the private adult and other education establishments received the lowest average monthly pay of Php6,883. See Table A for the average monthly compensation per paid employee by industry group.
Table A. Average Monthly Compensation Per Paid Employee By Industry Group: 2003
PSIC Code Industry Description Average Monthly Compensation Per Paid Employee M811 Private elementary education Php7,468 M812 Private secondary education Php10,252 M813 Private technical and vocational post-secondary non-degree education Php7,697 M814 Private higher education Php14,141 M815 Private adult and other education Php6,883 Top earners are establishments engaged in private higher education services
-
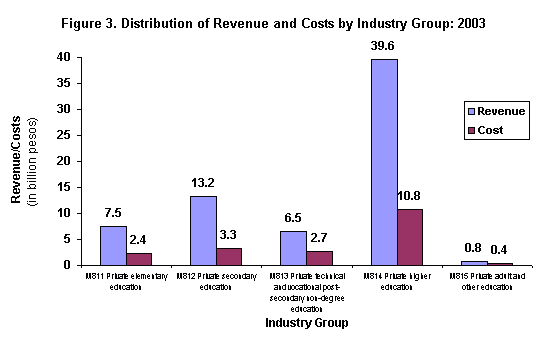
Total revenue reported by the sector in 2003 amounted to Php67.6 billion. Private higher education establishments generated the highest revenue of Php39.6 billion or 58.6 percent of the total. Private secondary education establishments followed with Php13.2 billion (19.5%). Private adult and other education generated the least revenue with Php863.9 million (1.3%). Figure 3 displays the distribution of revenue and costs by industry group.
-
Excluding compensation paid to employees in 2003, the total costs spent by the sector reached Php19.6 billion. Private higher education (PSIC M814) establishments incurred the biggest costs amounting to Php10.8 billion or 55.1 percent of the total. Private secondary education establishments (PSIC M812) ranked second with Php3.3 billion (16.7%). Private adult and other education (PSIC M815) spent the least with Php407.6 million (2.1%).
Gross additions to fixed assets reaches Php10.7 billion
-
Gross additions to fixed assets of private education service establishments reached Php10.7 billion. Private higher education establishments recorded the highest with Php7.0 billion (65.7%).
Total change in inventories amounts to Php27.5 million
-
Total change in inventories in 2003 summed up to Php27.5 million. Highest change in inventories which comprised 84.5 percent of the total change in inventories was reported by private higher education establishments.
Subsidies totals to Php343.9 million
-
The government provided Php343.9 million as subsidies to the sector during the year 2003. Private secondary education establishments received the highest subsidy with Php182.8 million or 53.2 percent of the total.
Labor productivity per worker is Php0.27 million
-
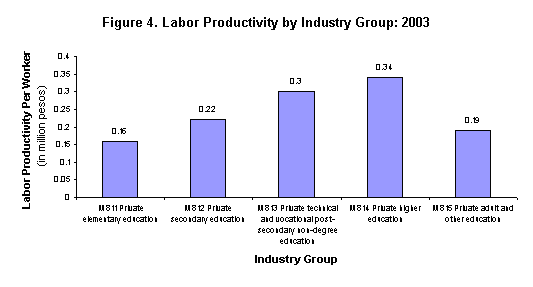
Revenue per worker, a measure of labor productivity was valued at Php0.27 million. The highest labor productivity at Php0.34 million was attained by private higher education. On the other hand, the lowest labor productivity at Php0.16 million was exhibited by establishments engaged in private elementary education. Figure 4 shows labor productivity by industry group. See also Tables R1 to R3 for other economic indicators.
TECHNICAL NOTES
Scope and Coverage
The 2003 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) formerly known as Annual Survey of Establishments (ASE) was conducted to collect information on the structure and trends of economic activities in the entire country for the year 2003. Covered were establishments engaged in economic activities as defined under the 1994 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). These establishments were classified into 14 sectors, one of which is on private education establishments (Sector M). The sector is composed of establishments engaged in private elementary education (M811); private secondary education (M812); private technical and vocational post-secondary non-degree education (M813); private higher education (M814) and private adult and other education (M815).
All private education establishments nationwide with average total employment (ATE) of 100 and over were covered on a 100 percent basis and those with ATE less than 100 were selected using simple random sampling.
Response
A total of 750 or 93.05% responded out of the 806 samples drawn for the sector. Adjustments for non-response were made through imputations.
Concepts and Definition of terms
Establishment is an economic unit, which engages under a single ownership or control, i.e. under a single legal entity, in one, or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location.
Economic activity or business is the activity of the establishment as classified under the1994 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). The main activity refers to the activity that contributes the biggest or major portion of the gross income or revenue of the establishment.
Total Employment is the number of persons who worked in or for the establishment as of November 15, 2003.
Paid employees are all persons working in the establishments receiving pay as well as those working away from the establishment when paid by and under the control of the establishment. Included are persons working as full-time or part-time and those employees on sick leave, paid vacation or holiday. Excluded are consultants, home workers and workers receiving commission only.
Unpaid workers include working owners who do not receive regular pay, apprentices and learners without regular pay, and persons working without regular pay for at least one third of the working time normal to the establishment.
Salaries and wages are payments in cash or in kind, prior to deduction for employee's contribution to SSS/GSIS, withholding tax, etc. Included are total basic pay, vacation, sick, maternity leave pay, overtime pay, and other benefits.
Revenue refers to cash received and receivables for goods sold and services rendered.
Cost refers to all expenses excluding compensation incurred during the year whether paid or payable. Valuation should be at market price including taxes and other charges, net of discounts, rebates, returns and allowances. Goods received from and services rendered by other establishment of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Gross additions to fixed assets refer to the cost of acquisition of fixed assets acquired in 2003 less the value of sales of fixed assets during the year.
Fixed assets are physical assets expected to have productive life of more than one year and intended for use and/or being used by the establishment. Included are land, buildings, fixtures, machinery, tool, furniture, office equipment, vehicles, and the like.
Capital expenditures refer to the cost of acquisition of fixed assets acquired in 2003 whether or not full payments have been made.
Subsidies are special grants in the form of financial assistance or tax exemption or tax privilege given by the government to develop an industry or production and to protect it against competition.
Inventories refer to stocks of goods owned by or under the control of the establishment as of a fixed date, regardless of where the stocks are located. Valuation should be at current replacement cost in purchaser's price at the indicated dates. Replacement cost is the cost of an item in terms of its present price rather than its original price.
Change in Inventories as a derived indicator is computed as the value of ending inventory less the value of beginning inventory.
Value Added is the total revenue plus capital expenditures (own account) plus change in inventories less total costs (net of indirect taxes, interest expenses, depreciation and bad and doubtful debts).
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
