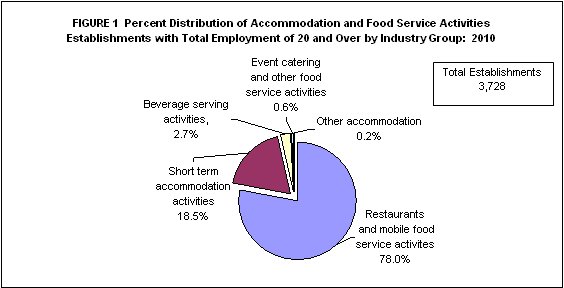
Restaurants and mobile food service activities dominate Accommodation and Food Service Activities section
Based on the preliminary results of the 2010 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) conducted nationwide, with 2010 as the reference year, the Philippines had a total of 3,728 establishments with total employment (TE) of 20 and over engaged in Accommodation and Food Service Activities. Figure 1 shows that restaurants and mobile food service activities garnered the highest number of establishments at 2,906 (78.0%) followed by short term accommodation activities with 691 establishments or 18.5 percent. Other accommodation recorded the lowest number of establishments with 7 or 0.2 percent only. (Table 1)
Most establishments are located in the National Capital Region
On the regional level, National Capital Region (NCR) had the most number of establishments with 1,839 (49.3%). CALABARZON (Region IVA) placed second with 379 (10.2%) establishments, Central Luzon (Region III) followed with 321 establishments (8.6%). Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) had the least with only 4 establishments (0.1 %). (Table 2)
Restaurants and mobile food service activities generate the highest employment
As for employment in 2010, a total of 190,688 employees were employed in Accommodation and Food Service Activities section. Figure 2 shows that 188,383 or 98.8 percent were paid employees while the remaining 2,305 (1.2%) were working owners and unpaid workers.
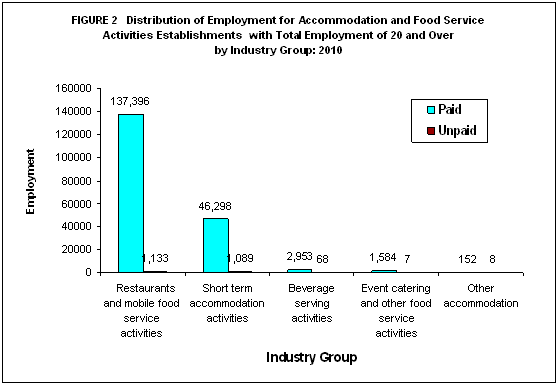
Table 1 shows that restaurants and mobile food service activities, having the largest share in terms of number of establishments, had the most number of employees with 138,529 (72.6%). Short term accommodation garnered 24.9 percent or 47,387 employees. The remaining 4,772 or 2.5 percent were distributed to beverage serving activities, event catering and other food service activities, and other accommodation.
Region wise, NCR was the top employer among regions with 97,722 employees (51.2%). CALABARZON followed with 18,038 employees (9.5%), and Central Visayas (Region VII) with 15,882 (8.3%). ARMM registered the least with only 140 employees or 0.1 percent. (Table 2)
Restaurants and mobile food service activities pay the highest compensation
The total compensation paid by Accommodation and Food Service Activities amounted to PHP23.7 billion, an equivalent of PHP125,893 average annual compensation per paid employee.
By industry group, restaurants and mobile food service activities paid the highest compensation to its employees amounting to PHP14.2 billion or 60.0 percent of the total. Short term accommodation activities paid PHP8.9 billion or 37.7 percent. Those working in other accommodation received a total compensation of PHP23.5 million or 0.1 percent of the total compensation. (Table 1)
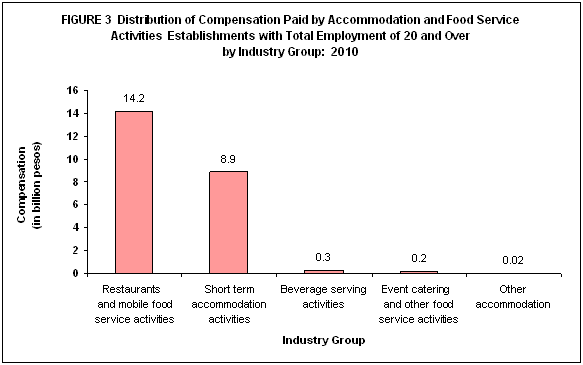
Table 2 shows that labor payments in NCR amounted to PHP14.3 billion or 60.5 percent of the total compensation paid nationwide. Central Visayas spent PHP2.0 billion or 8.4 percent followed by CALABARZON with PHP1.8 billion (7.4%). ARMM was the least payer with only PHP12.2 million (0.1%).
Short term accommodation activities employees earn the highest in 2010
Short term accommodation activities employees were the highest earners in 2010 with an average annual compensation of PHP193.1 thousand per paid employee. Employees of other accommodation received an average annual remuneration of PHP154.7 thousand. The lowest earners were employees from beverage serving activities with only PHP96.4 thousand average annual compensation. (Table 3)
By region, employees from MIMAROPA received the highest average annual compensation of PHP153.2 thousand per paid employee, closely followed by NCR with PHP148.7 thousand average annual compensation. Central Visayas ranked third with PHP127.5 thousand, while the least earners were employees from Northern Mindanao (Region X) with PHP64.7 thousand average annual compensation. Table 4 shows the average annual compensation per paid employee by region.
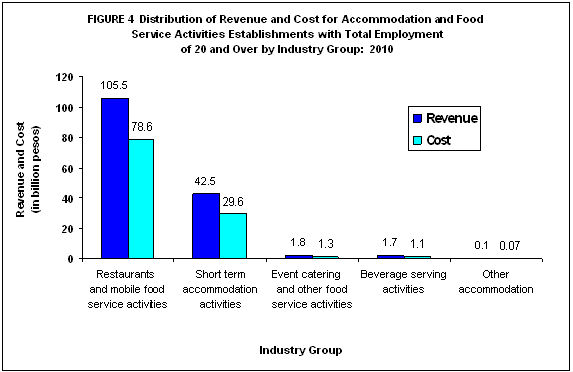
Total revenue amounts to PHP151.7 billion; Restaurants and mobile food service activities produce the largest revenue
Gross revenue earned in 2010 by Accommodation and Food Service Activities section reached PHP151.7 billion. Restaurants and mobile food service activities was the top contributor with PHP105.5 billion or 69.6 percent of the total. Short term accommodation activities generated PHP42.5 billion (28.0%). The remaining 2.4 percent was distributed to event catering and other food service activities, beverage serving activities and other accommodation.
With respect to regions, NCR produced the highest revenue amounting to PHP88.6 billion (58.4%) followed by CALABARZON with PHP12.9 billion or 8.5 percent. Completing the top three was Central Visayas with PHP12.3 billion or 8.1 percent of the total revenue. The least revenue was made by ARMM with PHP28.6 million.
Total cost reaches PHP110.7 billion; Restaurants and mobile food service activities spend the highest
Cost for operating the industry summed up to PHP110.7 billion. Restaurants and mobile food service activities disbursed the highest cost of PHP78.6 billion (71.0%). Short term accommodation activities incurred a total cost of PHP29.6 billion or 26.8 percent. Having the lowest number of establishments, other accommodation spent PHP70.8 million or 0.1 percent.
By region, NCR spent the largest as it incurred PHP63.9 billion (57.8 %) for operating the industry. CALABARZON followed with PHP9.1 billion (8.2%) then Central Visayas with PHP8.8 billion or 8.0 percent. As expected, the least cost was recorded by ARMM with only PHP19.4 million.
Revenue-cost ratio amounts to 1.37; Other accommodation record the highest returns
Revenue-cost ratio, the revenue generated per PHP1 cost, amounted to 1.37. Among industries, other accommodation recorded the highest with PHP1.58 revenue per PHP1 cost. Beverage serving activities followed with PHP1.57 revenue per PHP1 cost.
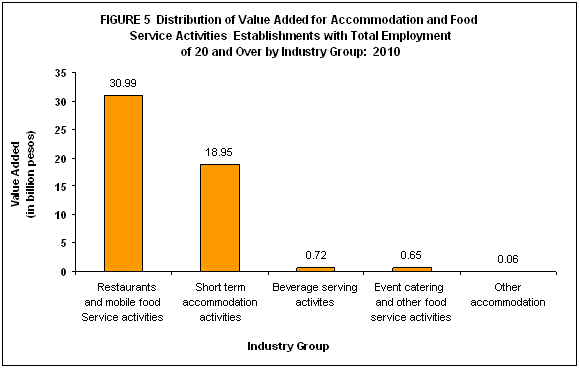
Value added amounts to PHP51.4 billion
Value added was estimated at PHP51.4 billion for Accommodation and Food Service Activities. Total value added of restaurants and mobile food service activities was recorded at PHP31.0 billion or 60.3 percent. Short term accommodation activities had a total value added of PHP18.9 billion or (36.9%). The least value added was accounted for by other accommodation with PHP60.3 million (0.1%).
Event catering and other food service activities employees are the most productive
Value added per worker, a measure of labor productivity, was valued at an average of PHP269.3 thousand per employee. Among industries, event catering and other food service activities had the highest average at PHP406.6 thousand, next was short term accommodation activities with PHP399.9 thousand while for restaurants and mobile food service activities, at PHP223.7 thousand.
Gross additions to tangible fixed assets totals PHP9.3 billion
Gross additions to tangible fixed assets in 2010 totaled to PHP9.3 billion. By industry, short term accommodation activities recorded the highest amounting to PHP6.9 billion (74.6%). Restaurants and mobile food service activities had PHP2.3 billion (24.8%) while the least gross additions to tangible fixed assets was recorded by event catering and other food service activities with PHP9.2 million or 0.1 percent.
Total change in inventories amounts to PHP298.2 million
Change in inventories, defined as the value of ending inventory less beginning, amounted to PHP298.2 million for the sector in 2010. Restaurants and mobile food service activities recorded the highest with PHP224.0 million, while short term accommodation had PHP75.2 million.
TECHNICAL NOTES
Introduction
The 2010 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) is a continuing activity of the National Statistics Office (NSO) which aims to provide key measures on the performance, levels, structure and trends of economic activities in the entire country for the year 2010. It is one of the designated statistical activities of the government and as such the survey generates the most critical and essential statistics required for economic planning and analysis.
The 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC) was adopted for the first time in this round. This is the latest version of the classification of industries in the country released by the NSCB after the 1994 PSIC was amended in 2002. It conforms with the International Standard Industrial Classification (ISIC) Revision 4 prescribe by the United Nations, but with modifications to suit national situation and requirement. The PSIC is a statistical classification of all economic activities, designed as a guide and a comprehensive framework for securing uniformity and comparability of both the government and private sectors.
The conduct of the ASPBI is governed by legislative acts and presidential directives, specifically Commonwealth Act No. 591 which was approved on August 19, 1940.
Scope and coverage
The 2010 ASPBI covered establishments engaged in 18 economic sections classified under the 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC) namely:.
-
Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing
-
Mining and Quarrying
-
Manufacturing
-
Electricity, Gas, Steam and Air Conditioning Supply and Water Supply
-
Water Supply; Sewerage, Waste Management and Remediation Activities
-
Construction
-
Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles
-
Transport and Storage
-
Accommodation and Food Service Activities
-
Information and Communication
-
Financial and Insurance Activities
-
Real Estate Activities
-
Professional, Scientific and Technical Activities
-
Administrative and Support Service Activities
-
Private Education
-
Human Health and Social Work
-
Arts Entertainment, and Recreation
-
Other Service Activities
The scope of the ASPBI was confined to “formal sector” only, which consists of the following:.
-
Corporations and partnership
-
Cooperatives and foundations
-
Single proprietorships with employment of 10 or more
-
Single proprietorships with branches
Like all other establishment surveys conducted by the NSO, the 2010 ASPBI used establishment as the unit of enumeration. It is defined as “an economic unit under a single ownership or control, i.e. under a single legal entity, engaged in one or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location.”"
Classification of Establishments
Before the actual selection of samples, the establishments listed in the frame were classified based on economic organization EO), legal organization (LO), industrial classification, employment size, and geographic location.
Economic organizations relates to the organizational structure or role of the establishment in the organization. The following are the types of economic organization:
-
Single establishment is an establishment which has neither branch nor main office
-
Branch only is an establishment which has a separate main office located elsewhere
-
Establishment and main office, both located in the same address and with branches elsewhere
-
Main office only is the unit which controls, supervises and directs one or more establishments of an enterprise
-
Ancillary unit other than main office is the unit that operates primarily or exclusively for a related establishment or group of related establishments or its parent establishment and provides goods or services that support but do not become part of the output of those establishments
The legal organization provides the legal basis for ownership of the establishment. The following are the types of legal organization:
-
Single Proprietorship refers to a business establishment organized, owned, and managed by one person, who alone assumes the risk of the business enterprise. The establishment name is that of a person, or it has words such as Owner, Proprietor or Operator
-
Partnership refers to an association of two or more individuals for the conduct of a business enterprise based upon an agreement or contract between or among them to contribute money, property or industry into a common fund with the intention of dividing profits among themselves. The establishment name includes words such as Owners , Partners, Limited or LTD., Associates or ASSOCS
-
Government Corporation is a private corporation organized for private aim, benefit or purpose and owned and controlled by the government. The establishment name included words such as Corporation or CORP., INCORPORATED or INC
-
Private Corporation is a corporation organized by private persons. The establishment name includes words such Corporation or Corp, Incorporated or INC
-
Cooperative - the establishment name includes words such as Cooperative or COOP
The legal organization provides the legal basis for ownership of the establishment. The following are the types of legal organization:
-
Single Proprietorship refers to a business establishment organized, owned, and managed by one person, who alone assumes the risk of the business enterprise. The establishment name is that of a person, or it has words such as Owner, Proprietor or Operator
-
Partnership refers to an association of two or more individuals for the conduct of a business enterprise based upon an agreement or contract between or among them to contribute money, property or industry into a common fund with the intention of dividing profits among themselves. The establishment name includes words such as Owners , Partners, Limited or LTD., Associates or ASSOCS
-
Government Corporation is a private corporation organized for private aim, benefit or purpose and owned and controlled by the government. The establishment name included words such as Corporation or CORP., INCORPORATED or INC
-
Private Corporation is a corporation organized by private persons. The establishment name includes words such Corporation or Corp, Incorporated or INC
-
Cooperative - the establishment name includes words such as Cooperative or COOP
The industrial classification of an economic unit is determined by the activity from which it derives its major income or revenue. The 2009 PSIC is utilized to classify units according to their economic activities. It was approved for adoption by government agencies and instrumentalities through NSCB Resolution No. 2 Series 2010 signed on February 10, 2010. It will be used for the 1st time for the ASPBI.
The 2009 PSIC consists of an alpha character and 5 numeric digits. The alpha character, which represents the major section, is denoted by the characters A to U. They also refer to sector classification. The first two numeric digits represent the division; the first three numeric digits, the group; the first four digits, the class; and the 5 digits, the sub-class.
The size of the establishment is determined by its total employment (TE). The following are the employment size classification used in the 2010 ASPBI:
| 0 | 1 - 4 | 5 | 100 - 199 |
| 1 | 5 - 9 | 6 | 200 - 499 |
| 2 | 10 - 19 | 7 | 500 - 999 |
| 3 | 20 - 49 | 8 | 1000 - 1999 |
| 4 | 50 - 99 | 9 | 2000 & Over |
| TE Code | Total Employment | TE Code | Total Employment |
The geographic or physical location of the establishments was classified in accordance with the Philippine Standard Geographic Code (PSGC) as of December 31, 2010 which contains the latest updates on the number of regions, provinces, cities, municipalities and barangays in the Philippines.
The geographic domains of the 2010 ASPBI for establishments with TE of 20 and over are the 17 administrative regions while the whole country serves as the geographic domain for establishments with TE of less than 20.
Hence, the samples of the 2010 ASPBI with TE of 20 and over shall provide data for 17 administrative regions. For samples with TE of less than 20, the data that will be presented is limited only at the national level.
Response Rate
A total of 932 or 93.9 percent of sample establishments responded. These include receipts of “good” questionnaires, partially accomplished questionnaires, reports of closed, moved out or out of scope establishments.
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
Economic activity or business is the activity of the establishment as classified under 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). Generally, the main activity of the establishment is the establishment's principal source of income. If the establishment is engaged in several activities, its main activity is that which earns the biggest income or revenue.
Total employment is the number of persons who worked in or for this establishment as of November 15, 2010.
Paid employees are all persons working in the establishment and receiving pay, as well as those working away from the establishment paid by and under the control of the establishment. Included are all employees on sick leave, paid vacation or holiday. Excluded are consultants, home workers, workers receiving pure commissions only, and workers on indefinite leave.
Salaries and wages are payments in cash or in kind to all employees, prior to deductions for employee’s contributions to SSS/GSIS, withholding tax, etc. Included are total basic pay, overtime pay, and other benefits.
Revenue is the value of goods, products/by-products sold and/or services rendered to others whether paid in cash or is considered receivable by the establishment. Valuation of products/by products sold should be in producer’s price (ex-establishment), net of discounts and allowances, including duties and charges but excluding subsidies. It also include goods transferred and/or services rendered to other establishment belonging to the same enterprise as the said establishment which should be treated as sales or as if sold to a customer; and revenue from products on a contractual basis from materials supplied by the establishment.
Cost refers to all expenses excluding compensation incurred during the year whether paid or payable. Valuation should be at purchaser’s price including taxes and other charges, net of discounts, rebates, returns and allowances. Goods received from and services rendered by other establishment of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Fixed assets are physical assets expected to have productive lives of more than one year and intended for use and/or being used by the establishment. Included are land, buildings, other structures and land improvements, transport equipment, machinery and equipment, furniture, fixtures, and other fixed assets.
Book value of tangible fixed assets is the initial value or acquisition cost of tangible fixed assets less the accumulated depreciation.
Gross additions to tangible fixed assets is the sum of cost of new and used fixed assets acquired during the year, cost of alteration and improvements done by others and cost of fixed assets produced by the establishment less the value of sales of fixed assets during the year.
Valued added is gross output less intermediate input. Gross output for accommodation and food service activities is the sum of the total revenue (less interest income, rent income from land, dividend income, royalty income and franchise income), capital expenditures of fixed assets produced on own account and change in inventories. Intermediate input is equal to the sum of the following cost items: materials and supplies purchased; fuels, lubricants, oils and greases purchased; electricity and water purchased; cost of industrial services done by others; cost of non-industrial services done by others; goods purchased for resale; research and experimental development expense; environmental protection expense; royalty fee; franchise fee and other cost.
Inventories refer to the stocks of goods owned by and under the control of the establishment as of a fixed date, regardless of where the stocks are located. Valuation should be at current replacement cost in purchaser’s price at the indicated dates. Replacement cost is the cost of an item in terms of its present price rather than its original price.
Change in Inventories is equivalent to the total value of inventories at the end of the year less the value at the beginning of the year.
Subsidies are special grants in the form of financial assistance or tax exemption or tax privilege given by the government to aid and develop an industry or production and to protect it against competition.
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
