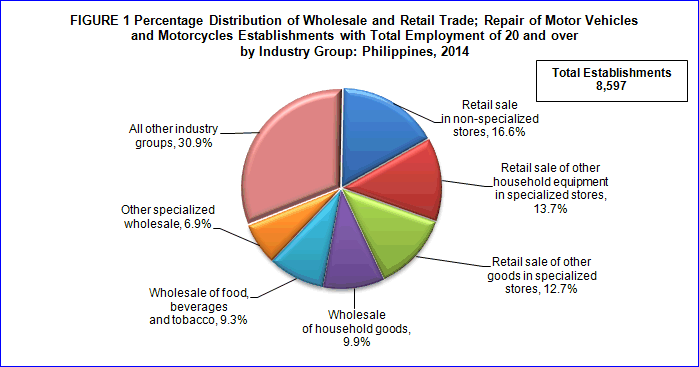
Retail sale of other goods in specialized store accounts for majority of establishments
The 2014 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) preliminary results counted a total of 8,597 establishments with total employment (TE) of 20 and over, engaged in wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles.
As shown in Figure 1, retail sale in non-specialized stores garnered the highest number of establishments which accounted 1,425 or 16.6 percent of the total number. Retail sale of other household equipment in specialized store ranked second with 1,174 (13.7 %). Establishments engaged in retail sale of other goods in specialized stores came in third with 1,091 or 12.7 percent.
Regional distribution of the establishments showed that NCR has concentrated 3,687 number of establishment (42.9%). Neighboring region of CALABARZON placed second with 863 establishments (10.0%), followed by Central Visayas with 709 (8.2%) while ARMM had the least number with 9 establishments among regions.
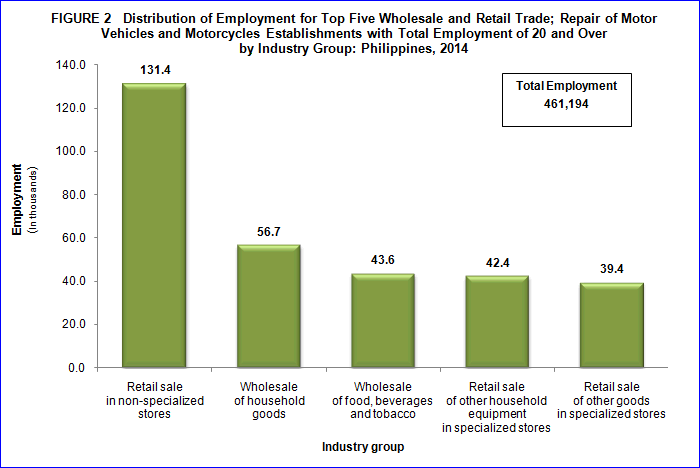
Retail sale in non-specialized stores hire the highest number of workers
Employment in 2014 engaged a total of 461,194 workers of which 459,579 (99.6%) were paid workers and the rest were working owners and unpaid workers.
Retail sale in non-specialized stores with 131,402 workers (28.5%); wholesale of household goods with 56,746 workers (12.3%); and wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco with 43,627 (9.5%) have provided half of the total employment (50.2%) or 231,775 workers to the labor force of the sector.
Among regions, NCR was the top employer with 218,897 workers or 47.5 percent, followed by CALABARZON with 41,725 employees or 9.0 percent. Central Visayas came in a small margin with 40,831 workers or 8.9 percent. On the other hand, ARMM recorded the least with 330 workers.
The average number of workers per establishment of the sector was marked at 54. Retail sale in non-specialized stores recorded the highest at the average of 92, followed by retail sale of motor vehicles at 72. Retail sale of automotive fuel in specialized stores at an average of 28 posted the lowest.
Labor payments reach to PHP81.7 billion
The wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles sector paid a total disbursement worth PHP81.7 billion in 2014, equivalent to an average annual compensation of PHP177.7 thousand per employee.
By industry group, retail sale in non-specialized stores spent the highest compensation expenditures amounting to PHP18.3 billion or 22.4 percent of the total. Wholesale of household goods was second with PHP14.9 billion or 18.3 percent. Wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco ranked third with PHP7.9 billion (9.8 percent). Non-specialized wholesale trade recorded the lowest payments of PHP71.5 million (0.1%).
Across regions, employers in NCR paid out the biggest share in total compensation amounting to PHP50.9 billion (62.3%). CALABARZON placed second providing an amount of PHP6.7 billion (8.3%) while businesses in Central Visayas region disbursed PHP5.2 billion (6.4%). Workers in ARMM received the lowest compensation of PHP21.3 million.
Workers of retail trade not in stores, stalls or markets are highest-paid employees in 2014
Workers in wholesale of household goods received the highest average annual compensation of PHP263.7 thousand. On the other hand, workers employed in wholesale of agricultural raw materials and live animals received the lowest payment of PHP113.6 thousand. Figure 3 shows the five leading industries in terms of average annual compensation for wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles.

At regional level, NCR employers provided the highest average annual compensation to its employees in the amount of PHP233.1 thousand, while ARMM employers provided the lowest payments of PHP64.6 thousand.
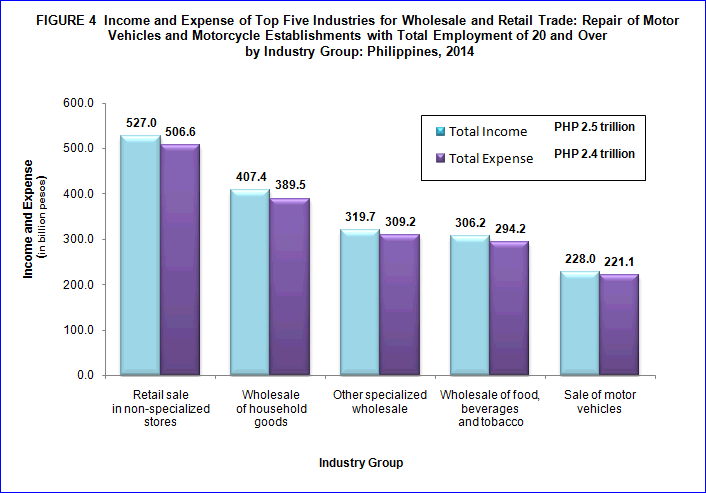
Retail sale in non-specialized stores contribute the largest share in income and expense
Gross revenue earned in 2014 for the sector reached PHP2.5 trillion, while total expense incurred cost PHP2.4 trillion in 2014.
Retail sale in non-specialized stores earned the highest income of PHP527.0 billion (21.3%), followed by wholesale of household goods with PHP407.4 billion (16.4%). Other specialized wholesale ranked third with PHP319.7 billion (12.9%) return. Likewise, retail sale in non-specialized stores had incurred the largest expenditures of PHP506.6 billion (21.3%). Wholesale of household goods and other specialized wholesale spent PHP389.5 billion (16.4%) and PHP309.2 billion (13.0%) overheads respectively.
By region, NCR establishments earned more than half (57.9%) of the total income of the sector amounting to PHP1.44 trillion. Other high-income regions were the following: CALABARZON with PHP247.0 billion (10.0%), Central Luzon with PHP157.7 billion (6.4%) and Central Visayas with PHP136.4 billion (5.5%). In the same way, NCR incurred also highest expense amounting to PHP1.38 trillion (58.0%). Other regions with highest expense reported were as follows: CALABARZON PHP237.3 billion (10.0%), Central Luzon PHP149.5 billion (6.3%) and Central Visayas PHP130.5 billion (5.5%).
Income- expense ratio yields a 1.04 turnover
The income per peso expense generated a ratio of 1.04 in 2014. Among industries, wholesale on a fee or contract basis, wholesale of machinery, equipment and supplies and retail sale of information and communications equipment in specialized stores exhibited the highest with 1.07 exceeding the sector average ratio. Sale of motor vehicle parts and accessories and retail sale of other household equipment in specialized stores have trailed with 1.06 income-expense ratio. On the other hand, sale of motor vehicles, other specialized wholesale and retail sale of automotive fuel in specialized stores have recorded the lowest ratio of 1.03.
At the regional level, Northern Mindanao posted an income-expense ratio of 1.07, Cordillera Autonomous Region at 1.06, and Central Luzon, Western Visayas and Central Visayas at 1.05.
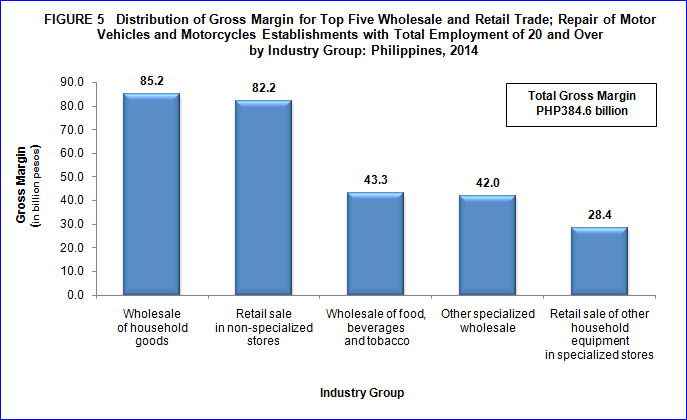
Gross margin reaches PHP384.6 billion
Gross margin (or trade margin) in 2014, reached PHP384.6 billion output. The top three combined industries reached more than half (54.9%) of the total gross margin of the section and these were the following:
- Wholesale of household goods, with PHP85.2 billion (22.2%);
- Retail sale in non-specialized stores, with PHP82.2 billion (21.4%); and
- Wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco, with PHP43.3 billion (11.3%).
The top three grosser in the regional level accounting for 78.3 percent of the total gross margin were NCR with 242.8 billion (63.1%), CALABARZON with PHP36.6 billion (9.5%) and Central Luzon with PHP21.8 billion (5.7%).
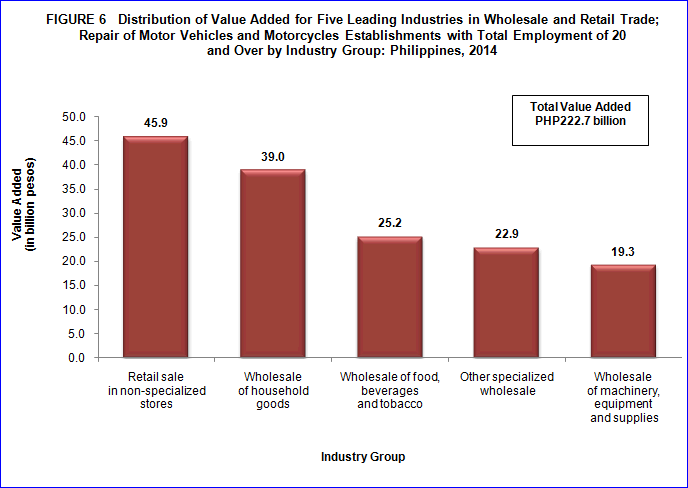
Value added amounts to PHP222.7 billion
During the survey period, value added generated by wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles sector was estimated at PHP222.7 billion in 2014.
Top three industries that contributed almost half (49.4%) to the total value added of the sector were the following: retail sale in non-specialized stores with PHP45.9 billion (20.6%), wholesale of household goods with PHP39.0 billion (17.5%) and wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco with PHP25.2 billion (11.3%).
At the regional level, NCR contributed the largest value added of PHP132.7 billion (59.6%).
Other specialized wholesale industry has the highest labor productivity
Value added per employee measure the labor productivity of the sector and was estimated at PHP484.7 thousand. Other specialized wholesale industry recorded the highest among industries with PHP810.2 thousand while maintenance and repair of motor vehicles generated the lowest with PHP211.2 thousand. Workers from NCR were the most productive among regions with PHP607.4 thousand.
Gross additions to fixed assets accumulates to PHP13.6 billion
The sector acquired PHP13.6 billion gross addition (capital expenditures less sale of fixed assets) in 2014. Retail sale in non-specialized stores amassed the biggest gross addition to fixed assets with PHP4.1 billion (30.2%) while retail trade not in stores, stalls or markets had the least with PHP1.3 million. In the regions, NCR recorded the highest additions amounting to PHP7.4 billion.
Total change in inventories amount to PHP42.2 billion in 2014
Total change in inventories (defined as ending less beginning inventory) of the sector amounted to PHP42.2 billion in 2014. Wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco had the highest inventories comprising 24.5% or PHP10.3 billion of the total. Retail sale in non-specialized stores and wholesale of household goods posted PHP7.6 billion (17.9%) and PHP7.4 (17.5%) respectively.
Among regions, NCR had the highest share in change in inventories at PHP27.0 billion (63.9%) while ARMM garnered the lowest of PHP5.8 million.
Government grants PHP4.7 billion subsidies
Subsidies are special grants received from the government in the form of financial assistance or tax exemption or tax privilege to aid and develop an industry. Total subsidies received from the government amounted to PHP4.7 billion in 2014.
Wholesale of food, beverages and tobacco industry and retail sale in non-specialized stores both located in NCR, received PHP4.4 billion and PHP358.0 million from the government, respectively.
Sales from e-commerce reaches PHP1.8 billion
Transactions from e-commerce (sales) reached PHP1.8 billion in 2014. The three industries from NCR posted e-commerce transactions and these were the following:
- Wholesale of household goods, with PHP642.3 million (35.1%);
- Retail sale of other goods in specialized stores, with PHP396.2 million (21.6%); and
- Retail trade not in stores, stalls or markets, with PHP306.0 million (16.7%).
TECHNICAL NOTES
Introduction
This Special Release presents the preliminary results of the 2014 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) for the Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles sector for establishments with total employment of 20 and over in the formal sector of the economy.
The 2014 ASPBI is one of the designated statistical activities of the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA). Data collected from the survey will provide information on the levels, structure, performance and trends of economic activities of the formal sector of the economy for year 2014. It will also serve as benchmark information in the measurement and comparison of national and regional economic growth.
The survey was conducted nationwide in April 2015 with the year 2014 as the reference period of data, except for employment which is as of November 15, 2014..
Establishment Data Management System (EDMS) was still utilized in the decentralized processing of 2014 ASPBI questionnaires in the province as well as the online accomplishment of questionnaire through the PSA website. .
Data are presented at the national, regional and industry group or 3-digit 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC)..
Legal Authority
The conduct of the 2014 ASPBI is authorized under Republic Act 10625 known as the Philippine Statistical Act of 2013 - Reorganizing and strengthening of the Philippine Statistical System (PSS), its agencies and instrumentalities.
Scope and Coverage
The 2014 ASPBI is a nationwide undertaking confined to the formal sector of the economy and as such excluded the informal sector. The following comprise the formal sector:
- Corporations and partnerships
- Cooperatives and foundations
- Single establishment with employment of 10 or more
- Single proprietorship with branches
Hence, the 2014 ASPBI covered only the following economic units:
- All establishments with total employment (TE) of 10 or more, and;
- All establishments with TE of less than 10, except those establishments with Legal Organization = 1 (single proprietorship) and Economic Organization = 1 (single establishment), that are engaged in economic activities classified according to the 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC).
The initial estimate of the 2014 LE shows that there are about 944,500 establishments in operation in the country for the year. About 266,000 establishments (28% of the total establishments) belong to the Formal Sector of which 231,000 (87%) comprise the establishment frame.
Listed below are the 18 economic sectors within the scope of the 2014 ASPBI classified under the 2009 PSIC.
- Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing (A)
- Mining and Quarrying (B)
- Manufacturing (C)
- Electricity, Gas, Steam, and Air Conditioning Supply (D)
- Water Supply; Sewerage, Waste Management and Remediation Activities (E)
- Construction (F)
- Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair and Maintenance of Motor Vehicles, Motorcycles (G)
- Transportation and Storage (H)
- Accommodation and Food Service Activities (I)
- Information and Communication (J)
- Financial and Insurance Activities (K)
- Real Estate Activities (L)
- Professional, Scientific and Technical Activities (M)
- Administrative and Support Service Activities (N)
- Education (P)
- Human Health and Social Work Activities (Q)
- Arts, Entertainment and Recreation (R)
- Other Service Activities (S)
Sampling Design
Unit of Enumeration
The unit of enumeration for the 2014 ASPBI is the establishment. An establishment is defined as an economic unit, which engages, under a single ownership or control, in one or predominantly one kind of activity at a single fixed physical location.
Classification of Establishments
An establishment is categorized by its economic organization (EO), legal organization (LO), industrial classification, employment size and geographic location.
Economic Organization (EO) refers to the organizational structure or role of the establishment in the organization.
Legal Organization (LO) refers to the legal form of the economic entity that provides the legal basis for ownership of the establishment.
Industrial Classification is determined by the activity from which it derives its major income or revenue. The 2009 PSIC which was approved for adoption by government agencies and instrumentalities through NSCB Resolution No. 2 Series 2010 was utilized to classify economic units according to their economic activities.
Size (SZ) of the Unit of Enumeration is determined by its total employment (TE) as of specific date. Total employment (TE) refers to the total number of persons who work in or for the establishment. This includes paid employees, working owners, unpaid workers and all employees who work full-time or part-time including seasonal workers. Included also are persons on short term leave such as those on sick, vacation or annual leaves and on strike.
Geographic Classification is grouping of establishments by geographic area using the Philippine Standard Geographic Code (PSGC) classification. The PSGC contains the latest updates on the official number of regions, provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays in the Philippines. The PSGC as of December 31, 2014 was used for the 2014 ASPBI.
Sampling Design
Selection of sample establishment for the 2014 ASPBI was done using stratified systematic sampling with 3-digit or 5-digit PSIC serving as industry strata and employment size as the second stratification variable.
Estimation Procedure
For Establishments with TE of 20 and Over
a. Non-Certainty Stratum (strata of TE 20 to 49 and TE 50 to 99) for Sections G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R and S.
The estimate of the total of a characteristic for the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over for an industry domain in each region
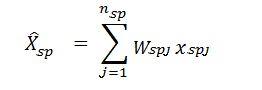
where:
s = denotes the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over
p = 1,2,...17 regions (geographic domains)
Xspj = value of the jthestablishment in the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over in for an industry domain in each regionin each region
j = 1,2,3,..., nsp establishments
Wspj = weight of the jth establishment in non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over for an industry domain in each region
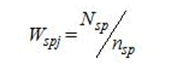
Nsp = total number of establishments in the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over for an industry domain in each region
nsp = number of sample establishments in the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over for an industry domain in each region
b. Certainty Stratum

where:
c = denotes the certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over
p = 1,2,...17 regions (geographic domains)
Xcpj = value of the jthestablishment in the non-certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over in for an industry domain in each region
j = 1,2,3,..., mcp establishments
mcp = number of establishments in the certainty employment strata in TE of 20 and over in an industry domain within each region
c. Total Estimate for TE of 20 and Over
The estimate of the total of a characteristic for the industry domain in each region (geopraphic domain) was obtained by aggregating the estimated for all employment strata (non-certainty and certainty) in the same industry domain,
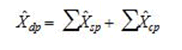
where dp denotes the industry domains in each region
National level estimate of the the characteristic by industry domain were obtained by aggregating separately the estimates for the particular industry domain from all the regions,
Weight Adjusment Factor for Non-Response
To account for non-response in the non-certainty strata, the adjusment factors, and (n/n') was multipled with the sampling weight (W) of each of the sampling unit. The sampling weight which is defined as N/n was recomputed as

Thus, the adjusted weight (W'sj) for employment stratum in TE 1-9 or TE 10-19 was

Where:
Ns = total number of establishments in employment stratum in TE 1-9 or TE 10-19 in the Sth industry domain
n's = number of responding establishments in the employment stratum in TE 1-9 or TE 10-19 Sth industry domain
For the non-certainty employment stratum for the selected industry domain with TE of 20-99, the adjusted weight (W'spj) was
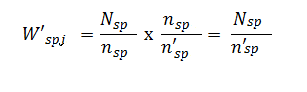
Where:
Nsp = total number of establishments in the non-certainty employment stratum with TE 20-99 for the selected industry domain within each geographic domain (region)
n'sp = number of responding establishments in the non-certainty employment stratum with TE of 20-99 for the selected industry domain within each geographic domain (region)
Response Rate
Field operations of the 2014 ASPBI were scheduled from April to July 2015.
Total response rate for Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles sector was 87.9 percent (3,909 out of 4,445 establishments). This included receipts of "good" questionnaires, partially accomplished questionnaires, reports of closed, moved out or out of scope establishments.
Of the total responses, 96 establishments responded online.
Concepts and Definitions of Terms
Establishment is an economic unit under a single ownership control, i.e., under a single entity, engaged in one or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location.
Total Employment is the number of persons who worked in for the establishment as of November 15, 2014.
Paid employees are all full-time and part-time employees working in or for the establishment and receiving pay, as well as those working away from the establishment and paid by and under the control of the establishment. Included also are all employees on sick or maternity leave, paid vacation or holiday and on strike. Excluded are directors paid solely for their attendance at meetings, consultants, workers on indefinite leave, working owners who do not receive regular pay, home workers and workers receiving pure commissions only.
Unpaid workers are working owners who do not receive regular pay, apprentices and learners without regular pay and persons working for at least 1/3 of the working time normal to the establishment without regular pay. Excluded are silent or inactive business partners.
Compensation is the sum of salaries and wages, separation, terminal pay and gratuities paid by the establishment to its employees and total employer’s contribution to SSS/GSIS, ECC, PhilHealth, Pag-ibig, etc.
Salaries and wages are payments in cash or in kind to all employees, prior to deductions for employee’s contributions to SSS/GSIS, withholding tax, etc. Included are total basic pay, overtime pay and other benefits.
Income or Revenue includes cash received and receivables for goods/products and by-products sold and services rendered. Valuation is at producer prices (ex-establishment) net of discounts and allowances, including duties and taxes but excluding subsidies.
Cost refers to all expenses excluding compensation incurred during the year whether paid or payable. Valuation should be at purchaser price including taxes and other charges, net of discounts, rebates, returns and allowances. Goods received from and services rendered by other establishment of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Expense refers to cost incurred by the establishment during the year whether paid or payable. This is treated on a consumed basis. Valuation is at purchaser price including taxes and other charges, net of rebates, returns and allowances. Goods and services received by the establishment from other establishments of the same enterprise are valued as though purchased.
Intermediate cost refers to expenses incurred in the production of goods such as materials and supplies purchased, fuels purchased, electricity purchased and industrial services done by others plus beginning inventory of materials, supplies and fuels less ending inventory of materials, supplies and fuels.
Value Added is gross output less intermediate input. Gross output for Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles is the sum of the total revenue (less interest income, rent income from land, dividend income, royalty income and franchise income), capital expenditures of fixed assets produced on own account and change in inventories. Intermediate input is equal to the sum of the following expense items: materials and supplies purchased; fuels, lubricants, oils and greases purchased; electricity purchased, water purchased; expense of industrial services done by others; expense of non-industrial services done by others; goods purchased for resale; research and development expense; environmental protection expense; royalty fee; franchise fee and other expense.
Gross addition to tangible fixed assets is equal to capital expenditures less sale of fixed assets, including land.
Change in total inventories is computed as the total of ending inventory less the total beginning inventory.
Inventories refer to the stock of goods owned by and under the control of the establishment as of a fixed date, regardless of where the stocks are located. Valuation is at current replacement cost in purchaser prices. Replacement cost is the cost of an item in terms of its present price rather than its original cost.
E-Commerce refers to the selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet Protocol-based networks and other computer networks, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) network, or other on-line system.
