5-MONTH TOTAL TRADE GROWS BY 6.5 PERCENT
Total trade in goods for January to May 2000 amounted to $27.047 billion which was 6.5 percent higher than $25.391 billion last year. Payments for merchandise imports rose by 3.2 percent to $12.841 billion from $12.445 billion in 1999. On the other hand, exports posted a 9.7 percent increase with an aggregate revenue of $14.206 billion, up from $12.945 billion last year. The balance of trade in goods (BOT-G) amounted to $1.365 billion which was a 173.0 percent jump from $500.0 million a year ago.
Fig. 1. Philippine Foreign Trade by Month: 2000
(F.O.B. Value in Million US Dollar)

MAY IMPORTS DECLINE BY 3.8 PERCENT
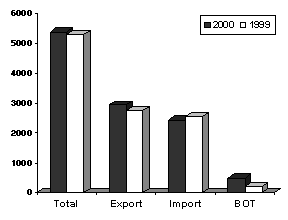
Merchandise trade for the month of May 2000 alone grew by 1.7 percent to $5.368 billion from $5.280 billion in 1999. Export receipts amounted to $2.931 billion, increasing by 6.7 percent from $2.747 billion last year, while import expenditures declined by 3.8 percent to $2.437 billion from $2.533 billion. The BOT-G surplus for the country stood at $494 million.
Fig. 2A. Philippine Trade Performance in Jan � May : 1999 & 2000
(F.O.B. Value in Million US Dollar)
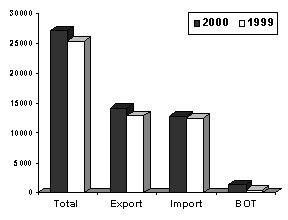
Fig. 2B. Philippine Trade Performance in May : 1999 & 2000
(F.O.B. Value in Million US Dollar)
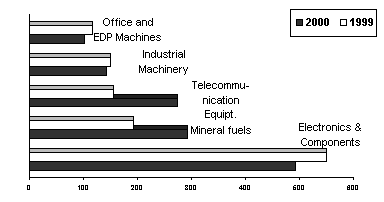
ELECTRONICS & COMPONENTS DIP BY 10.3 PERCENT
Accounting for 20.2 percent of the aggregate import bill, payments for Electronics and Components amounted to $492.31 million which was 10.3 percent lower than $548.89 million last year.
Purchases of Mineral Fuels, Lubricants and Related Materials ranked second with a 12.0 percent share. Payments reached $292.71 million for a 51.4 percent increase over $193.40 million last year.
Telecommunication Equipment and Electrical Machinery was the third top import with purchases reaching $274.75 million or a 75.6 percent increase from $156.51 million in 1999.
Industrial Machinery and Equipment accounted for 5.9 percent of the total bill and ranked fourth with payments of $142.59 million which was a 5.7 percent decline from $151.13 million last year.
Payments for Office and EDP Machines combined for a 4.2 percent share of the aggregate bill. However this fell by 12.7 percent to $102.17 million from $117.06 million a year ago.
Textile Yarn, Fabrics, Made-up Articles and Related Products accounted for 3.8 percent of the total and was sixth top import for the month. These were valued at $91.56 million which was 25.4 percent lower than $122.68 million last year.
Rounding up the list of the top imports for May 2000 were Transport Equipment $88.86 million; Iron and Steel, $82.84 million; Materials/Accessories Imported on Consignment Basis for the Manufacture of Other Electrical and Electronic Machinery and Equipment, $80.93 million; and Organic and Inorganic Chemicals, $59.73 million.
Aggregate payment for the top ten imports for the month amounted to $1.708 billion or 70.1 percent of the total bill.
Fig. 3. Top 5 Philippine Imports in May: 1999 & 2000
(F.O.B. Value in Million US Dollar)
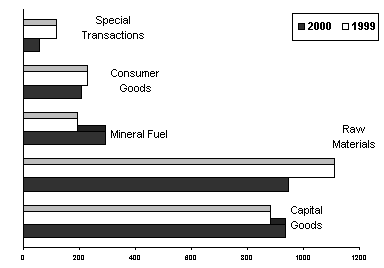
MINERAL FUELS & CAPITAL GOODS GROW
Payments for Raw Materials and Intermediate Goods consisting of unprocessed and semi-processed raw materials fell by 14.8 percent year-on-year to $944.31 million from $1.108 billion. Its share of the aggregate bill was placed at 38.8 percent.
Capital Goods accounted for 38.3 percent of the aggregate bill as importation grew by 5.9 percent to $934.06 million from $881.82 million last year.
Purchases of Mineral Fuels & Lubricants valued at $292.71 million registered a 51.4 percent increase from $193.40 million a year ago.
Expenditures for Consumer Goods and Special Transactions amounted to $206.32 million and $59.50 million, respectively.
Fig. 4. Philippine Imports by Major Type of Goods in May : 1999 & 2000
(F.O.B. Value in Million US Dollar)
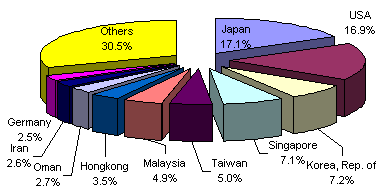
JAPAN ACCOUNTS FOR 17.1 PERCENT OF IMPORT BILL
Japan shipped 17.1 percent of the total May 2000 imports despite a drop of 11.2 percent to $416.71 million from $469.23 million a year ago. Exports to Japan on the other hand amounted to $408.25 million yielding a two-way trade figure of $824.96 billion and a BOT-G deficit placed at $8.46 million.
The United States was second with a 16.9 percent share, reporting shipments of $412.07 million against purchases of $829.54 million. Total trade reached $1.242 billion while a BOT-G trade surplus stood at $417.47 million.
Republic of Korea followed at third even as imports decreased by 16.3 percent to $175.85 million from $210.03 million while revenue from exports reached $88.43 million resulting to a total trade of $264.28 million and an $87.42 million BOT-G deficit.
Other major sources of imports for the month were Singapore, $173.92 million; Taiwan, $121.25; Malaysia, $120.58 million; Hongkong, $85.35 million; Oman, $65.77 million; Iran, $63.82 million; and Germany, $60.92 million.
Payment for imports from the top ten sources for the month amounted to $1.696 billion or 69.6 percent of the total.
Fig. 5. Philippine Imports by Country in April : 2000
UNCOLLECTED DOCUMENTS
As of press time 96 out of 57,755 export documents and 112 out of 54,661 import documents are still expected from the ports.
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
