SUMMARY REPORT OF THE EXTERNAL TRADE PERFORMANCE FOR SEPTEMBER 1999
(Preliminary)
BOT-G SURPLUS GROWS TO $2.450 BILLION
The country's balance of trade in goods (BOT-G) surplus for the first three quarters of 1999 placed at $2.450 billion, posted a 354.4 percent reversal from a deficit level of $962.0 million while total trade grew by 9.0 percent to $48.667 billion from $44.652 billion a year earlier. Payments for imported merchandise went up by 1.3 percent to $23.108 billion from $22.807 billion while receipts from export of goods grew by 17.0 percent to $25.558 billion from $21.845 billion a year earlier (See Fig. 2A).
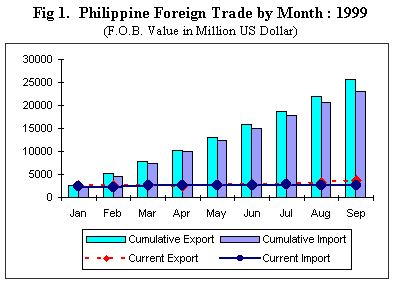
For September 1999, the country's BOT-G surplus surged by 244.9 percent to $1.145 billion from last year's $332.0 million. Receipts from exports went up by 32.6 percent to $3.693 billion from $2.786 billion while total expenditure for foreign-made goods increased by 3.8 percent to $2.548 billion from last year's $2.454 billion. Total trade valued at $6.241 billion improved by 19.1 percent from $5.240 billion last year (See Fig. 2B).

BILL FOR ELECTRONICS AND COMPONENTS UP BY 16.2 PERCENT
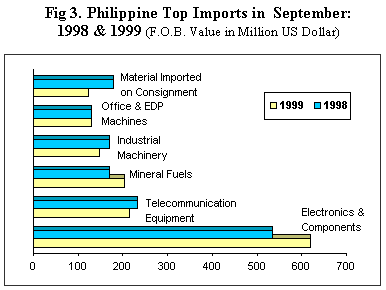
Payments for Electronics and Components, still the country's top import with a 24.3 percent share, rose by 16.2 percent to $620.4 million from $533.74 million last year.
Bills for Telecommunication Equipment and Electrical Machinery, the second top imported items with an 8.5 percent share and valued at $216.05 million fell by 7.4 percent from $233.19 million last year.
Expenditures for Mineral Fuels, Lubricants and Related Materials,comprised the third top import. Accounting for 8.0 percent of the total bill, payments reached $202.82 million, up by 19.4 from $169.84 million in 1998.
Fourth top import for the month consisted of Industrial Machinery and Equipment. Payments, accounting for 5.8 percent of the total, dropped by 12.9 percent to $148.15 million from $170.09 million.
Office and EDP Machines, accounting for 5.0 percent of the total, emerged as the fifth top import with a value of $128.63 million, down by 0.6 percent from $129.34 million in 1998.
Materials/Accessories Imported on Consignment Basis for the Manufacture of Other Electrical and Electronic Machinery and Equipmentaccounted for 4.8 percent of the aggregate bill even as purchases dropped by 31.6 percent to $123.20 million from $180.20 million (See Fig. 3).
Other top imports for the month in review were: Transport Equipment,$102.68 million; Textile Yarn, Fabrics, Made-up Articles and Related Products, $96.25 million; Iron and Steel, $85.37 million; Plastics in Primary and Non-Primary Forms, $54.28 million.
Payments for the countrys top ten imports for the month in review amounted to $1.778 billion, or 69.8 percent of the total.
PAYMENTS FOR CAPITAL GOODS REACH $1.060 BILLION
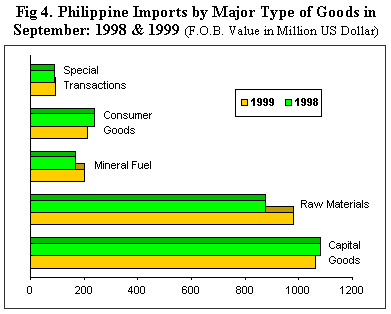
Accounting for 41.6 percent of the import bill, Capital Goods emerged as the country's top purchase for the month with aggregate payment reaching $1.060 billion, or 2.0 percent lower than the year-ago mark placed at $1.081 billion.
Close behind was the Raw Materials and Intermediate Goods-group which accounted for the second biggest slice of the import bill for the month placed at 38.6 percent. Actual payments amounted to $982.62 million, up by 12.3 percent from $874.96 million last year.
Purchases of Mineral Fuel and Lubricant valued at $202.82 million grew by 19.4 percent from $169.84 million in 1998.
Expenditures for Consumers Goods fell by 11.7 percent to $210.35 million while payments for Special Transactions inched up by 2.7 percent to $92.83 million (See Fig. 4).
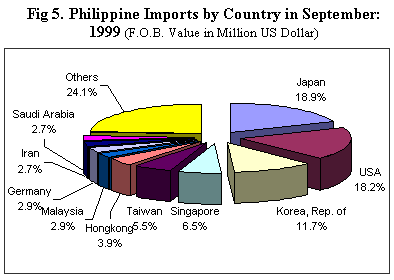
JAPAN CORNERS 18.9 PERCENT OF AGGREGATE BILL
Japan, emerged as RPs biggest source of imports with an 18.9 percent share. Total payment for Japanese-made goods amounted to $482.15 million while receipts from exports to Japan reached $412.06 million. Total trade reached $894.21 million and the BOT-G deficit for RP stood at $70.09 million.
With an 18.2 percent share of the total import bill, purchases of US-made goods came out as the countrys second top imports for the month. Payments declined by 5.9 percent to $464.82 million, down from $493.80 million last year. Exports to the US, on the other hand, amounted to $987.67 million yielding a two-way trade figure of $1.452 billion and a BOT-G surplus of $522.85 million for RP.
The third biggest source of imports for the month was the Republic of Korea. Expenditures for imports amounted to $297.01 million while revenue for exports reached $120.43 million resulting in a two-way trade value of $417.44 million and a $176.59 million BOT-G deficit for RP.
Other major sources of imports for September 1999 were: Singapore,$165.01 million; Taiwan, $140.72 million; Hongkong, $100.35 million;Malaysia, $73.78 million; Germany, $73.35 million; Iran, $69.98 million; and,Saudi Arabia, $68.26 million.
Payments for imports from the top ten sources amounted to $1.935 billion or 76.0 percent of the total (See Fig. 5).
UNCOLLECTED DOCUMENTS
As of press time 97 out of 55,947 export documents and 85 out of 56,687 import documents are still expected from the ports.
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
