The 2019 Survey on Information and Communication Technology (SICT) was undertaken nationwide and covered the 18 sectors in the 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). This special release presents the final results of the 2019 SICT for Non-core ICT industries. Non-core ICT industries exclude the Information and Communication sector, and some industries in the Manufacturing sector, the Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles sector, and the Other Service Activities sector, which are under the Core ICT industries.
1. Number of establishments that owned and used computers and communication equipment was recorded at 94.8 percent
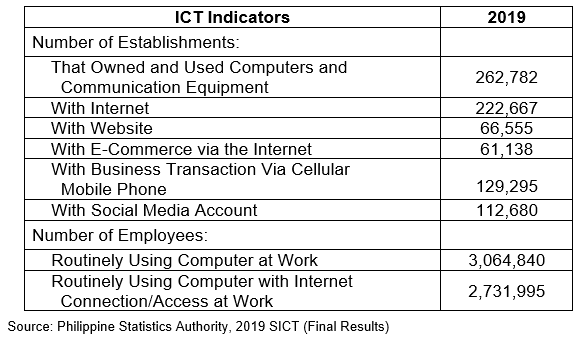
A total of 277,323 establishments in the non-core ICT industries were recorded in 2019. Of this number, 262,782 or 94.8 percent owned and used computers and communication equipment in their business operations. (Table 1)
Among the sectors, Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles led in terms of number of establishments that owned and used computers and communication equipment with 109,830 or 41.8 percent share to the total. This was followed by Financial and Insurance Activities with
2. Eight in ten establishments had internet connection or access in 2019
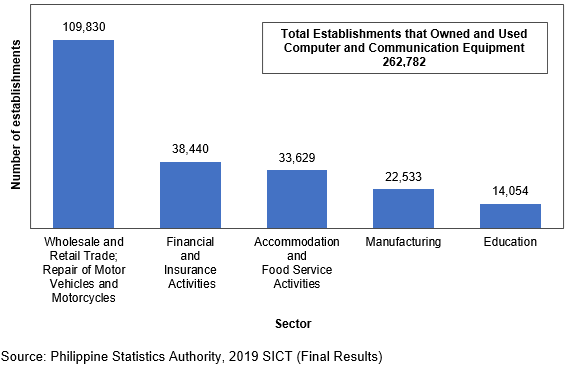
The total number of establishments with internet connection or access in the non-core ICT industries was 222,667 or 80.3 percent in 2019. Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles posted the highest number of establishments with internet connection or access with 87,322 (39.2%). This was followed by Financial and Insurance Activities and Accommodation and Food Service Activities with 36,422 establishments (16.4%) and
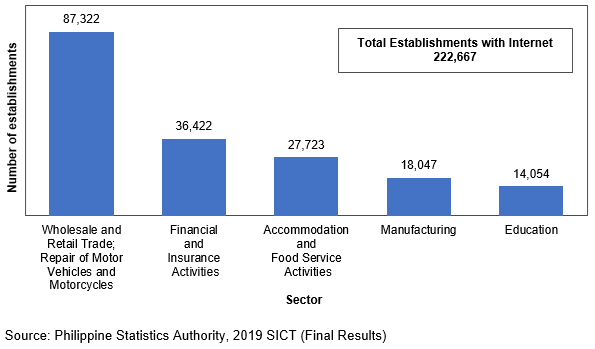
In 2019, 135,764 establishments in the non-core ICT industries used the Internet in downloading or requesting government forms. (Figure 3 and Table 7)
Among the sectors, Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles registered the highest number of establishments that used the Internet in downloading or requesting government forms with 47,551 establishments (35.0%). Meanwhile, Mining and Quarrying registered the least with
Internet was also used by establishments in the non-core ICT industries for the following activities:
a. Obtaining information from other organizations (112,749 establishments);
b. Sharing or distribution of information within the establishment (93,694 establishments);
c. Sharing or distribution of information with other organization (76,024 establishments);
d. Staff training (70,109 establishments); and
e. Internal or external recruitment (68,178 establishments). (Table 6)
3. About 66.56 thousand establishments had website
The number of establishments with website in the non-core ICT industries reached 66,555 in 2019.
By sector, Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles reported the highest number of establishments with website at
4. Accommodation and Food Service Activities posted the highest number of establishments with e-commerce transactions via the Internet
E-commerce transactions via the Internet was utilized by 61,138 establishments under the non-core ICT industries in 2019.
Accommodation and Food Service Activities had 15,341 establishments with e-commerce transactions via the Internet in 2019, the highest among the
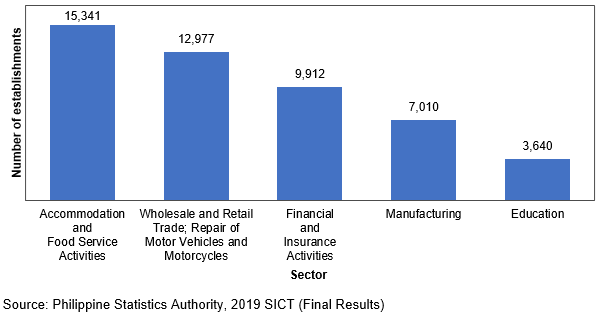
5. Employees of Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles were the most engaged in the use of mobile phones/smartphones in business transactions
A cellular mobile phone/smartphone is another medium that can be used for doing business. A total of 129,295 establishments engaged in the use of mobile phones/smartphones in their business transactions in 2019.
The top five sectors in terms of number of establishments which used mobile phones/smartphones in their business transactions in 2019 were:
a. Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles, 54,925 establishments or 42.5 percent;
b. Accommodation and Food Service Activities, 22,569 establishments or 17.5 percent;
c. Manufacturing, 13,306 establishments or 10.3 percent;
d. Financial and Insurance Activities, 13,173 establishments or 10.2 percent; and
e. Education, 4,821 establishments or 3.7 percent. (Table 5)
6. About four in ten establishments had social media accounts
Presence of social media accounts was recorded at 112,680 establishments under the non-core ICT industries in 2019.
Wholesale and Retail Trade; Repair of Motor Vehicles and Motorcycles (37,228 establishments) had the highest number of establishments with social media account, while Mining and Quarrying (66 establishments) had the least. (Table 8)
7. Around 3.1 million employees routinely used computer at work whereas 2.7 million routinely used computer with internet connection at work
At the national level, 3.06 million employees routinely used computer at work or 41.6 percent of the total employees for the non-core ICT industries in 2019. Moreover, 2.73 million employees routinely used computer with internet connection or access at work or 37.1 percent of the total.
By sector, Administrative and Support Service Activities led in terms of number of employees that routinely used computer at work and computer with internet connection or access at work with 986,003 and 968,275, respectively. On the other hand, Mining and Quarrying had the least number of 3,218 employees who routinely used computer at work and 3,100 employees who routinely used computer with internet connection or access at work. (Tables A and 2)
DENNIS S. MAPA, Ph.D.
Undersecretary
National Statistician and Civil Registrar General
TECHNICAL NOTES
Introduction
The 2019 Survey on Information and Communication Technology (SICT) was the eighth in the series of SICT conducted by the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA). It was a rider to the 2019 Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industry (ASPBI) conducted in 2020.
The 2019 SICT collected and generated information on the availability, distribution, and access/utilization of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) among establishments in the country.
Specifically, the survey measured the following:
a. component of ICT resources and their utilization by establishments;
b. diffusion of ICT into establishments from various sources;
c. e-commerce transactions from data on e-commerce sales/revenue and purchases;
d. cellular mobile phone business transactions from data on sales/revenue;
e. estimate of the number of ICT workers in establishments;
f. methods of disposal of ICT equipment; and
g. presence of social media accounts.
II. Data Collection and Processing
The 2019 SICT utilized only one type of questionnaire (SICT Form 1) for all sectors which was distributed to sample establishments by field office personnel. All information collected in the 2019 SICT refers to calendar year 2019, except for employment where reference period is as of 15 November 2019. The SICT Form 1 followed the 2017 SICT questionnaire design with minor revisions due to the addition of some data items and categories recommended by the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT).
Sample establishments were given various options in accomplishing the survey questionnaire, and these are:
a. Online Questionnaire, which can be accessed at https://sict.psa.gov.ph;
b. Electronic Questionnaire, which can be accomplished in fillable Portable Document Format (.pdf) or excel (.xlsx) file format; and
c. Printed Questionnaire, which is the traditional and physical version of the questionnaire.
The Establishment Data Management System (EDMS) was utilized in the decentralized processing of 2019 SICT questionnaires in the provinces.
III. Taxonomy of Establishments
An establishment is defined as an economic unit under a single ownership or control which engages in one or predominantly one kind of economic activity at a single fixed location. It is categorized by its economic organization, legal organization, industrial classification, employment size, and geographic location.
Economic Organization refers to the organizational structure or role of the establishment in the organization. It may be a single establishment, branch, establishment and main office with branches elsewhere, main office only, or an ancillary unit other than the main office.
Legal Organization refers to the legal form of the economic entity which owns the establishment. It may be a single proprietorship, partnership, government corporation, stock corporation, non-stock corporation, or cooperative.
Industrial classification of an economic unit was determined by the activity from which it derives its major income or revenue. The 2009 PSIC which was approved for adoption by government agencies and instrumentalities through PSA Resolution No. 01 Series of 2017-158 signed on 14 February 2017 was utilized to classify economic units according to their economic activities.
Size of an establishment is determined by its total employment as of the time of visit during the latest Updating of the List of Establishments.
Total Employment (TE) refers to the total number of persons who work in or for the establishment. This includes paid employees, working owners, unpaid workers and all employees who work full-time or part-time including seasonal workers. Also included are persons on short-term leave such as those on sick, vacation or annual leaves and on strike.
Geographic Classification refers to the grouping of establishments by geographic area using the Philippine Standard Geographic Code (PSGC) classification. The PSGC contains the latest updates on the official number of regions, provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays in the Philippines. The PSGC as of 31 December 2019 was used for the 2019 SICT.
IV. Scope and Coverage
The 2019 SICT was undertaken nationwide and covered all industries in the 2019 ASPBI as classified in the 2009 Philippine Standard Industrial Classification (PSIC). For the purpose of the survey, these industries were classified as core ICT industries and non-core ICT industries.
Non-core ICT industries exclude the information and communication sector, and some industries in the manufacturing, the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles, and the other service activities sectors, which were under the core ICT industries.
V. Sampling Design
The 2019 SICT utilized stratified systematic sampling design with 3-digit PSIC serving as industry strata (industry domain) and employment size as the second stratification variable, except for ICT Core and Business Process Management (BPM) industries which were at the 5-digit PSIC level.
Domain
The geographic domain of the core ICT industries is the region, while for the non-core ICT industries is at the national level. The industry domain/stratum for the non-core ICT industries are the 3-digit PSIC industry groups, while the core ICT industries are the 5-digit PSIC industry sub-classes. The employment domain/stratum is the Micro, Small, and Medium Establishments (MSME) classification.
Unit of Enumeration
The unit of enumeration of the survey is the establishment.
Sampling Frame of Establishments
The frame for the 2019 SICT was extracted from the preliminary 2019 List of Establishments (LE) as of 5 February 2020. Samples were selected from the list of samples of the 2019 ASPBI to ensure that the samples for the SICT are subset sample of ASPBI.
Estimation procedure
Non-core Industries
1) Estimation of Survey Weights
a) Base Weight
The base weight is the inverse of the probability of selection. For the SICT, the base weight for each domain is given by:
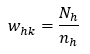
where:
whk = weight of the kth establishment in hth stratum
Nh = total no. of establishments in hth stratum
nh = total no. of sample establishments in hth stratum
h = refers to the industry-employment stratum
b) Adjusted Weight
Adjustment Factor Due to Non-Response
To take into account the non-responding sample establishments, the adjustment factor by region and industry domain is as follows:
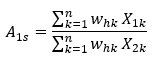
where:
A1s = adjustment factor for industry domain s
X1k = eligibility status of the kth sample establishment (1 if eligible, 0 otherwise)
X2k = responding status of the kth sample establishment (1 if responding, 0 otherwise)
Adjusted Weight
The adjusted weight is the product of the base weight and adjustment factor due to non-response. That is
![]()
where:
w1hk = adjusted weight of the kth sample establishment in stratum h
whk = base weight of the kth establishment in the hth stratum
A1s = adjustment factor for industry domain s
c) Final Weight
Adjustment Factor for Conformity with ASPBI
In order to conform with the estimate of total non-core ICT establishments in the ASPBI, final adjustment factor is computed as follows:
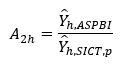
where:
A2h = adjustment factor for conformity with ASPBI = estimated number of establishments in stratum h in ASPBI
= estimated number of establishments in stratum h in ASPBI = preliminary estimated number of establishments in stratum h in SICT which is computed as:
= preliminary estimated number of establishments in stratum h in SICT which is computed as:
![]()
Final Weight
The final weight is the product of the adjusted weight and the second adjustment factor. That is,
![]()
where:
w'hk = final weight of the kth sample establishment in stratum h
w1hk = adjusted weight of the kth sample establishment in stratum h
A2h = adjustment factor for conformity with ASPBI
2) Estimation of Total
Total by Industry-Employment Stratum
The estimator for the total of a characteristic in each industry-employment stratum is given by:
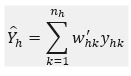
where:
yhk = sample value of the kth sample establishment in stratum h
whk = Final weight of the kth sample establishment in stratum h
Total by Industry Stratum
The estimator for the total of a characteristic in each industry stratum is given by:
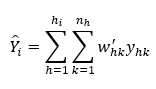
where:
hi = Number of employment strata for industry stratum i
Total by Employment Stratum
The estimator for the total of a characteristic in each employment stratum in a domain is given by:
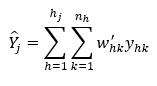
where:
hj = Number of industry strata for employment stratum j
National Total
The estimator for the national total of a characteristic is given by:
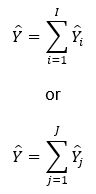
where:
I = Total number of industry strata
J = Total number of employment strata
VI. Response Rate
The overall response rate for the 2019 SICT was 78.1 percent (10,120 of the 12,959 sample establishments). This included receipts of good questionnaires, partially accomplished questionnaires, and reports of closed, moved out, or out-of-scope establishments. For Non-Core ICT industries, the response is 76.5 percent (6,939 of the 9,070 sample establishments). Out of the total responding establishments, 388 (3.0%) establishments responded online.
VII. Concepts and Definitions
E-commerce or electronic commerce refers to the sale of goods and services where an order is placed by the buyer, price, and terms of sale are negotiated over the Internet Protocol-based networks, an extranet, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) network, or other online systems.
Information Economy (IE) is a term used to describe the economic and social value created through the ability to rapidly exchange information anytime, anywhere, and to anyone. It is characterized by the intensive use by businesses of ICT for the collection, storage, processing, and transmission of information. The use of ICT is supported by supply of ICT products from an ICT-producing sector and through trade.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) as defined by the Commission on Information and Communication Technology (CICT) is "the totality of electronic means to collect, store, process and present information to end-users in support of their activities". It consists, among others, of computer systems, office systems, and consumer electronics, as well as network information infrastructure, the components of which include the telephone system, the Internet, fax machines, and computers.
ICT Resources are equipment, knowledge and human resources used to support electronic business/manufacturing processes and the conduct of electronic commerce transactions. It includes computer and peripheral equipment, systems and application software, network channels, telecommunication equipment, routers, satellite, and other ICT hardware used in electronic business and commerce transactions, ICT support services and ICT workers.
Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that interchange data by packet switching using the standardized Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). It is a "network of networks" that consists of millions of private and public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope that are linked by copper wires, fiber-optic cables, wireless connections, and other technologies. The internet carries various information resources and services, such as electronic mail, online chat, file transfer and file sharing, online gaming, and the inter-linked hypertext documents and other resources of the World Wide Web (WWW).
Intranet is a set of networks, using the Internet Protocol and IP-based tools such as web browsers and file transfer applications, that is, under the control of a single administrative entity. That administrative entity closes the intranet to all but specific, authorized users. Most commonly, an intranet is the internal network of an organization.
Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network covering a small physical area, like a home, office, or small group of buildings, such as a school, or an airport. Current LANs are most likely to be based on Ethernet technology. Each workgroup can get to its local printer. Note that the printers are not accessible from outside their workgroup.
Network channel is a collection of computers connected to each other that allows them to communicate with each other and share resources and information. All networks are made up of basic hardware building blocks to interconnect network nodes, such as Network Interface Cards (NICs), Bridges, Hubs, Switches, and Routers.
Web site is a collection of Web pages, images, videos, or other digital assets that is hosted on one or more web servers, usually accessible via the internet. All publicly accessible websites are seen collectively as constituting the "World Wide Web". The pages of a website can usually be accessed from a common root URL called the homepage, and usually reside on the same physical server.
Wide Area Network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a broad area (i.e., any network whose communications links cross metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries. Less formally, a WAN is a network that uses routers and public communications links. The largest and most well-known example of a WAN is the internet. A WAN is a data communications network that covers a relatively broad geographic area (i.e. one city to another and one country to another country) and that often uses transmission facilities provided by common carriers, such as telephone companies.
