IMPORTS GROW 10.6 PERCENT
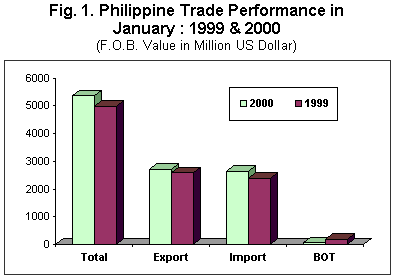
Total trade in goods between the Philippines and the rest of the world went up by 7.8 percent to $5.368 billion in January 2000 from $4.979 billion a year ago. Merchandise exports increased by 5.3 percent to $2.717 billion from $2.581 billion in 1999 while total imports rose by 10.6 percent to $2.651 billion from $2.398 billion last year. The January 2000 balance of trade in goods (BOT-G) fell to a surplus of $65.0 million from $182.0 million last year. (See Fig. 1).
ELECTRONICS & COMPONENTS INCREASE 9.5 PERCENT
Payments for Electronics and Components, still the top import with a 26.7 percent share, went up by 9.5 percent to $708.53 million from $647.01 million last year.
Imports of Mineral Fuels, Lubricants and Related Materials accounted for 9.4 percent of the total and amounted to $250.23 million which was 85.5 percent higher than $134.90 million in January 1999.
With a 7.9 percent share, in Telecommunication Equipment and Electrical Machinery valued at $210.01 million grew by 13.4 percent from $185.27 million a year ago.
The fourth top import consisted of Industrial Machinery and Equipment. Value of shipments accounting for 6.3 percent of the total dropped by 5.0 percent to $167.27 million from $176.04 million last year.
Materials/Accessories Imported on Consignment Basis for the Manufacture of Other Electrical and Electronic Machinery and Equipment comprised the fifth top import group. Accounting for 5.7 percent of the total bill, payments reached $151.54 million, which declined by 13.0 percent from $174.26 million a year earlier.
Transport Equipment, accounting for 5.2 percent of the total, emerged as the sixth top import with a value of $138.72 million which was 133.1 percent higher than $59.52 million last year. The large increase can be partly attributed to the importation of one aircraft worth $65.0 million. (See Fig. 2).
Rounding up the list of the top imports for January 2000 were Office and EDP Machines, $108.95 million; Textile Yarn, Fabrics, Made-up Articles and Related Products, $93.24 million; Iron and Steel, $67.24 million; and Organic and Inorganic Chemical, $48.25 million.
Aggregate payment for the top ten imports for the month amounted to $1.944 billion, or 73.3 percent of the total.

CAPITAL GOODS GAIN 16.2 PERCENT
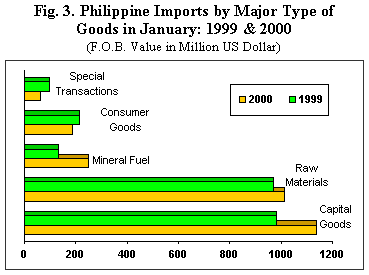
Accounting for 42.9 percent of the import bill, Capital Goods was the top purchase for the month with aggregate payments reaching $1.138 billion which was 16.2 percent higher than $979.44 million a year ago. The increase was partly due to the arrival of one (1) aircraft worth $65.0 million.
Raw Materials and Intermediate Goods accounted for the second biggest slice of the import bill at 38.2 percent. Actual payments amounted to $1.012 billion, which increased by 4.6 percent from $968.25 million last year.
Purchases of Mineral Fuel and Lubricant valued at $250.23 million went up by 85.5 percent from $134.90 million in 1999.
Expenditures for Consumer Goods fell by 13.7 percent to $186.45 million while payments for Special Transactions also dropped by 36.1 percent to $63.75 million.
21.1 PERCENT OF IMPORTS FROM THE US
With a 21.1 percent share of the total import bill, the United States (US) remained as the top source of foreign-made merchandise. Value of imports amounted to $559.84 million increasing by 5.2 percent from $532.41 million a year ago. Exports to the US, on the other hand, amounted to $801.87 million yielding a two-way trade figure of $1.362 billion and a BOT-G surplus of $242.03 million.
Japan, the second biggest source of imports with a 17.6 percent share, reported sales valued at $467.17 million against purchases amounting to $388.46 million. Total trade reached $855.63 million and a BOT-G deficit stood at $78.71 million.
The third biggest source of imports was the Republic of Korea. Expenditures for imports amounted to $254.61 million while revenues for exports reached $90.12 million resulting in a two-way trade value of $344.73 million and a $164.50 million BOT-G deficit.
Other major sources of imports for January 2000 were Hongkong, $170.36 million; Singapore, $163.78 million; Taiwan, $146.27 million; Malaysia, $95.34 million; Thailand, $68.65 million; People's Republic of China, $63.30 million; and Indonesia, $59.30 million.
Payments for imports from the top ten sources amounted to $2.049 billion or 77.3 percent of the total (See Fig. 4).

UNCOLLECTED DOCUMENTS
As of presstime 85 out of 52,506 export documents and 107 out of 53,448 import documents are still expected from the ports.
Source: National Statistics Office
Manila, Philippines
